您现在的位置是: 首页 > 正能量的句子 正能量的句子
英语常用句子形式_英语的常用句式
tamoadmin 2024-08-17 人已围观
简介1.英语口语常用表达句子2.英语八大时态的句式结构和用法3.英语的句子类型有哪几种?4.平常常见(常用)的英语句子有哪些?5.英语基本句型有哪些英语基本句型有五个:S+V, S+V+Cs, S+V+O, S+V+Oi+Od, S+V+Od+Co, 其共有特征是主谓结构(S+V)。 句子成分主要有四种:主语S、谓语动词V、补语(主语补语Cs,宾语补语Co)和宾语(直接宾语Od,间接宾语Oi)。 ●P
1.英语口语常用表达句子
2.英语八大时态的句式结构和用法
3.英语的句子类型有哪几种?
4.平常常见(常用)的英语句子有哪些?
5.英语基本句型有哪些
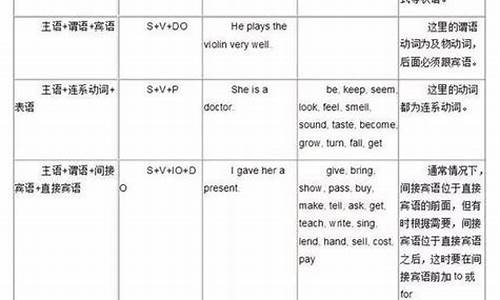
英语基本句型有五个:S+V, S+V+Cs, S+V+O, S+V+Oi+Od, S+V+Od+Co, 其共有特征是主谓结构(S+V)。
句子成分主要有四种:主语S、谓语动词V、补语(主语补语Cs,宾语补语Co)和宾语(直接宾语Od,间接宾语Oi)。
●Pattern 1 (S + V)
1. 此句型中,“V” 是不及物动词,后面无宾语,如:
My right arm hurts.
但通常有后续成分或称状语(A),即 S+V+A,如:
She lived hily.
The sun rises every morning.
2. 在有些句子中,主语或谓语或某一部分可省略,如:
(I) Hope to see you again soon.(省略主语)
Who called? Jane (did).(省略谓语)
●Pattern 2 (S + V + Cs)
1. 此句型的 “V” 是连系动词,“Cs” 是主语补语,或称表语。充当主语补语的有名词、代词、形容词、副词、数词、介词短语、动词 V-ing 形式或 V-ed 形式、不定式及名词性从句等,如:
My first name is Bill.
Life is colorful.
Seeing is believing.
Our belief is that things will improve.
2. 常见的连系动词有下列几类:
a. 表示“判断”:be;
b. 表示“变得”、“成为”:become, come, go, fall, get, grow, prove, turn 等;
c. 表示“保持着某一状态”:hold, keep, lie, remain, rest, sit, stay 等;
d. 表示“看起来”、“好像”:ear, look, seem 等;
e. 表示“实感”:feel, sound, taste, smell 等。
e.g. She is a teacher and I am a doctor.
Spring comes and all trees turn green.
He stayed awake all night.
You don’t look hy, what's the matter?
Their plan sounds wonderful.
●Pattern 3 (S + V + O)
1. “V” 是及物动词,后面需跟一个宾语,可充当宾语的有名词、代词、数词、不定式、V-ing 结构及名词性从句等,如:
I understand the program.
She asked to see the manager.
Mary is considering changing her job.
He said that he would call me tomorrow.
2. 这种结构有时必须跟状语,意义才完整(即 S + V + O + A),如:
We accepted their advice in buying a new car.
She completed the assignment just as the bell was ringing.
We don’t trust him because he often lies.
You make a promise only when you know you can keep it.
●Pattern 4 (S + V + Oi + Od)
1. 此句型的 “V” 称为双宾及物动词,其后需跟间接宾语 “Oi”(通常指人)和直接宾语 “Od”(通常指物或事)。
2. 此类动词大都具有给与的意义,常见的有allow, assign, award, bring, buy, cause, choose, fetch, find, get, give, grant, hand, lee, lend, offer, owe, pass, pay, post, promise, read, recommend, refuse, render, return, sell, send, show, sing, take, telephone, touch, tell, throw, wish, write 等,如:
I ge him the book.
I’ll return you the dictionary soon.
3. 有时间接宾语可移至直接宾语之后,但要加相应的介词如 “to”,“for”,“of” 等,试比较:
Betty ge her daughter an le.
→Betty ge an le to her daughter.
Father bought him a bike.
→Father bought a bike for him.
He asked me a question.
→He asked a question of me.
●Pattern 5 (S + V + Od + Co)
该句型中,谓语动词虽有宾语,但句子意义仍不完整,需加补语 “Co” 补足其意义。充当宾语补语的有名词、形容词、副词、介词短语、不定式短语及分词等,如:
We call him a fool.
We found the house empty.
Our neighbors built their wall high.
We believe you to be an honest man.
I heard them singing in the classroom.
常用的这类动词有:
oint, believe, call, catch, choose, consider, declare, elect, fancy, feel, find, hear, imagine, judge, keep, know, lee, make, name, need, prefer, prove, see, select, suppose, think, vote 等。
Noun Clause(名词从句)
名词从句包括主语、宾语、表语和同位语等从句。它们可以由下列连词引导:从属连词 that, whether, if;连接代词 who(ever), whom, whose, what(ever), which(ever);连接副词 when, where, why, how, how much / many /long /often 等。
●主语从句在句中作主语
That mathematics finds its use in every science is evident.
Whoever is tired may rest.
Why the earth moves round the sun is quite clear now.
主语从句常放在句尾而用 it 作形式主语使句子更加平衡,这时口语中常省略 that, 如上面第一句改成“It is evident (that) mathematics finds its use in every science.”更好。
在下列情况下必须把主语从句放在句尾而用 it 作形式主语:
1. 主句谓语是被动语态时,如:
It is said that he is a good doctor.
2. 主句是疑问句或感叹句时,如:
Is it true that the film star will come?
How wonderful it is that we'll visit the Great Wall tomorrow.
3. 主句谓语动词是 ear, turn out, hen, occur, come, strike, follow, matter 等时,如:
It hened that she had a cold and didn't go with us that day.
It turned out that I was wrong.
4. 表示说话人的推测或评价,如在 it seems, it may be, it is (un)likely, it is (im)possible, it is a pity, it is a wonder 等结构中,如:
It seems that this test is reliable.
It is a pity (that) she can't go with us.
5. 强调主句的表语时,如:
It is a mystery to me how it all hened.
It is necessary that he should do so.
●宾语从句在句中作宾语
I thought (that) you had read the book.
We should learn to tell whether an element is poisonous or not.
Do you know who invented this?
1. 宾语从句后有宾语补足语时常移至句末,而用 it 做形式宾语放在前面,如:
The experiment makes it clear that air has pressure.
2 宾语从句可作某些介词和某些作表语用的形容词的宾语,如:
The resistance of a wire also depends upon what material it is made of.
We are sure (that) it will be a success.
3. 宾语从句可以是直接引语也可以是间接引语,如:
He asked me, “Are you from Chengdu?”(直接引语)
He asked me whether I was from Chengdu.(间接引语)
●表语从句在句中作表语
The reason is (that) we hen't raised enough money.
That is what we want to know.
●同位语从句在句中作补充说明名词及其短语的从句
I am in dou whether I should buy or not.
He expressed his hope that he would visit China again.
Relative Clause(定语从句)
引导定语从句的关系词有
1. 关系代词 who, whom(代人);which(代物);that, whose, as (代人或物)。它们的数和人称要和先行词一致,格取决于它们在句中充当的成分,如:
A machine is a kind of device which (that) helps to do work.
Those who want tickets should go to the office.
The technician whom we met yesterday had worked out a new automatic device.
先行词前有限定词 all, any, every, (a)few, no, only, some, very 或序数词或形容词最高级等修饰时,或先行词是指物的不定代词 all, little, few,much, none 或 -thing 构成的复合不定代词时,一般只用关系代词 that,如:
Any boy that wants to succeed must work hard.
There is not much that can be done.
I've made up my mind, and nothing (that) you say will change it.
先行词是指示代词 such 或 same 时,只用 as, 先行词被指示形容词 such 或 same 修饰时,通常用as,如:
This book is not such as I expected.
She said the same as she said before.
I've never seen such dogs as you describe.
I'll wear the same dress as I did last time.
2. 关系副词有:when, where, why, 它们都在从句中作状语,其先行词总是表示时间、地点或理由的名词,如:
The days when they had to import grain from abroad he now passed.
Air moves from places where the pressure is higher to places where the pressure is lower.
He refused to tell the reason why he did it.
限制性和非限制性定语从句 (Restrictive and Non-restrictive Clause)
限制性定语从句是主句中的先行词不可缺少的一部分,如果省去,主句的意义就不完整或不明确,因此,它与主句关系十分密切,不用逗号与主句分开;非限制性定语从句只是对主句中的先行词作附加说明,如果省去,主句仍能表达明确、完整的概念,因此,它与主句间有一逗号分开,如:
Don't you know the people who live next door?
The problem, which is complicated, has been solved.
That 不用于引导非限制性定语从句;先行词是主句或主句的一部分时,用 which 或 as 引导非限制性定语从句,如从句放在主句之前则用 as 而不用which,如:
He changed his mind, which made me very angry.
He was a foreigner, as / which I knew from his accent.
As was expected, he performed the task with success.
关于 “Noun / Pronoun + Preposition + Which / Whom / Whose” 结构
The resistance of a conductor depends on the kind of substance of which it is made.
Isn't she the girl with whom you visited the exhibition the other day?
关系代词 whom 和 which 常常作介词 of 的宾语,用“名词/代词/数词+of+whom / which”结构,如:
He is reading a book, the name of which I don't know.
Her parents, both of whom are teachers, are very strict with her.
In our class there are forty students, four of whom are from Africa.
Whose 指物时常可用 of which 代替,这时 whose 所修饰的名词放在 of which 之前,如:
We had a meeting whose purpose was completely unclear.
= We had a meeting the purpose of which was completely unclear.
Apposition and Appositive Clause(同位语和同位语从句)
可以用作同位语的有:
1. 名词、代词、数词及其它们的短语、不定式和分词短语,如:
China, our great motherland, now is developing rapidly in science and technology.
We all went to see her.
We two are from Chongqing and they three are from Chengdu.
We all he a common desire — to become qualified teachers.
That's her job, taking care of the aged in the community.
2. of 引导的介词短语,如:
the city of Beijing, the art of writing
3. 用连词 or, or rather 或 or better 等引导的词或短语,如:
They arrived home late that evening or rather early the next morning.
4. 用插入语 that is (to say), in other words, namely, for example, for instance, such as, say, especially, particularly, chiefly, mainly 等引导的词或短语,如:
Mr. Smith knows five languages, namely English, French, Chinese, Russian and Japanese.
5. 同位语从句,即与先行词同位或等同的从句,其先行词多为belief, dou, fact, hope, idea, news, promise, question, remark, reply, report, thought, truth 等;其引导词多为 that(在口语中可省去),也可用 whether 等,如:
There can be no dou that we'll finish in time.
Most people are familiar with the idea that all matter consists of atoms.
We should discuss carefully the important question whether or not we can complete the task within a week.
注意 that 在同位语从句中不作任何句子成分,只起引导从句的作用,而在定语从句中 that 还充当主语或宾语,或状语,比较 :
No one can deny the fact that he has made great achievements in his work.(同位语从句,连词 that 在从句中不作任何 句子成分。)
This is the picture that the little boy drew yesterday. (定语从句,关系代词 that 在从句中作宾语。)
英语句子中的谓语动词必须和主语在人称和数上保持一致,如:
Mr. Smith teaches us oral English.
Nowadays lots of college graduates are busy looking for jobs.
1. 一些句子结构中的主谓一致:
a. 在 "there + be" 句型中,谓语动词通常和最邻近它的那个名词保持一致,如:
There is a book and four pens on the desk.
There are two beds and a bookshelf in the room.
b. 在定语从句中,谓语动词应和该从句的先行词保持一致,如:
Alice is the person who runs the school.
He who cheats on exams will be kicked out of the school.
I was one of those persons who were luckily interviewed by the director himself.
上例中如果 one 前有 the only 修饰,强调某一个体时,从句的谓语动词应用单
数,如:
I was the only one of those persons who was luckily interviewed by the director
himself.
c. 倒装结构中的谓语动词应与它的真正主语保持一致,如:
Here is a letter for you.
There come two buses.
2. 并列结构作主语时句子的主谓一致:
a. 由 both ... and ... 连接的两个名(代)词作主语时,谓语动词用复数,如:
Both Tom and Mary he been invited to the party.
b. 由 and 连接的并列结构作主语,谓语一般用复数。但当两个名词表达同一个人、
同一件事或同一概念时,谓语应该用单数,如:
The writer and editor is going to the meeting in person.
Bread and butter is a daily food in the west.
Law and order is so important to a country that no one should break it.
c. 由 as well as, as much as, along with, besides, in addition to, including, like, no
less than, rather than, (together) with 等连接的两个名(代)词作主语时,谓语应
和第一个名(代)词保持数的一致,如:
The bus driver as well as several passengers has survived the accident.
Yesterday I saw a pick-pocket with his company was caught by a policeman.
d. 由 or, either … or ..., neither … nor …, not only … but also … 等连接的两个名(代)词作主语时,谓语一般和后一个名(代)词保持一致,如:
Not you but I am to blame.
Neither you nor I am responsible for the whole thing.
3. 集体名词作主语时句子的主谓一致
a. cattle, police 作主语时,谓语动词总用复数,如:
Lots of cattle are raised on the grassland.
The police were searching for the criminals.
b. audience, board, class, committee, crowd, crew, enemy, family, ,
team 等作主语时,如果作整体看待,谓语动词用单数;若强调每一成员,谓语用
复数,如:
The committee consists of 12 members.
The committee hen't reached any agreement yet.
I am not sure where my family is.
My family care a lot about my study.
4. 一些代词作主语时句子的主谓一致:
a. 由 any, every, no 和 one, thing, body 构成的合成代词作主语时,谓语用单数,
如:
Nothing was found in the room.
Everyone has known the story.
b. both, few, several 和 many 作主语,表示复数的意义,所以谓语用复数,如:
Both are not quite so honest.
Many students trel during their vacations.
5. 带有数量修饰语的名(代)词作主语时句子的主谓一致:
a. 单数可数名词前有 every, each, many a 修饰、复数名词前有 each of, one of,
(n)either of, the number of 等修饰时,谓语用单数,如:
Many a student trels during his / her vacation.
The number of criminal cases in this city is increasing steadily.
One of us is to join the army.
b. 复数名词前有 a number of 或 one or two 修饰时,谓语用复数,如:
In this factory a number of workers are out of work now.
One or two plans are to be discussed.
c. 名词前有 a lot (of), lots (of), all (of), any (of), most (of), some (of), none (of),
more than one, 分数或百分数等修饰语时,谓语名词的数视中心名词的数而定,如:
Some of the butter has gone.
Some doctors are not well trained.
More than one picture was burned in the fire.
Half of it was damaged.
Half of them are here.
d. "数词+复数名词"作主语,若视为整体看待,表示距离、时间、价值、重量、长度
等时,谓语通常用单数,如:
Four years in the university is meaningful to me.
Two hundred dollars is too much to pay.
Five thousand miles is too far to trel.
e. "the+形容词"作主语表示某一类人时,具有复数意义,谓语用复数,如:
The old are to be taken good care of in this community.
英语口语常用表达句子
一、陈述句:是用来陈述一件事情或表示一种看法,可分为肯定句和否定句两种形式。
1、谓语动词是be动词,助动词he, has, will,情态动词can等时,只要直接在这些词后面加not就构成否定形式。
eg. Lily has already read this new book. (改为否定句)
Lily ______ ______ this new book ________.
2、谓语动词是行为动词而又没有助动词或情态动词时,必须在谓语动词前加助动词,一般现在时加助动词do ,第三人称单数加does,一般过去时加did,再和not构成否定结构。必须指出的是:don't, doesn't, didn't后都用动词原形。
eg.1)Jill has lunch at school every day. (改为否定句)
Jill _____ _____ lunch at school every day.
2)The children had a good time at the party. (改为否定句)
The children ______ _____ a good time at the party.
3)Rose didn't drink any milk this morning.(改为肯定句)
Rose ______ ______ milk this morning.
二、疑问句:是用来提出问题的句子。
A.一般疑问句:以be动词, he /has/do等助动词、can/may等情态动词开头,以yes或no来回答的问句。
它的基本结构是:Be/He /Has/Did等助动词(包括情态动词)+主语+谓语(包括表语)+┄?回答常用简略回答。
1、谓语动词是be动词、助动词、情态动词时,只要直接把这些词置于句首,句末改成问号。
eg. There's something wrong with his bike.(改成疑问句)
______ _____ _______ wrong with his bike?
2、谓语动词是行为动词时,必须在句首加上助动词Do、Does(三单)、Did(过去式)加上这些助动词后,句子中谓语动词必须用原形。
eg. 1)Edison built a science lab himself when he was ten. (改成疑问句)
______ Edison ______ a science lab himself when he was ten?
2)Those Japanese like Chinese food.(改成疑问句)
______ those Japanese ________ Chinese food?
注意:在把肯定句改成否定句或一般疑问句的时候,要注意句中是否有already、some、something、somebody等词,如果有也必须进行改变,already要改成yet,some、something、somebody等分别改成any、anything、anybody等。另外,在改成否定句的时候注意把too改成either,both改成neither,all改成none等.在改成一般疑问句的时候,常常把第一人称I、we改成第二人称you。
B.特殊疑问句:以疑问代词或疑问副词开头,提出疑问的句子。
它的基本结构是:特殊疑问词+一般疑问句语序。但是如果疑问词在句子中作主语或作主语的定语,就用特殊疑问词+陈述句语序。常用的疑问词有:what, who(whom), whose,which,when,where,how,why等,回答时针对问句中的代词和副词来回答,不用yes或no来回答。
1)对指物名词或谓语动词提出疑问,疑问词用what
①The twins were making a kite when their mother came in. (划线提问)
______ _____ the twins _____ when their mother came in?
②Mrs Turner asked her son to buy some eggs for supper. (划线提问)
_______ ______ Mrs Turner ask her son ______ _______?
2)对名词前定语提出疑问,疑问词应用which,而且必须和名词连用。
I'm going to take the shirt on the right.(划线提问)
______ _____ are you going to take?
3)对指人名词或代词提问用who,作宾语时提问用whom。
eg.Li Ping,they,his father
4)对物主代词和名词所有格提问用whose。
eg. Li Ping's coat→Whose coat my father→Whose father
5)对具体时间提出疑问,如 in the morning,last Sunday等,疑问词用when;对具体几点钟提问,疑问词应用what time。
6)对具体地点提出疑问,疑问词应用where。
The pupils are hing a picnic at the foot of the hill. (划线提问)
_____ _____ the pupils hing a picnic?
7)对表原因的从句提问,常见的有because引导的从句,疑问词应用why。
Xiao Cheng didn't go to the farm with us because he was ill. (划线提问)
_______ _____ Xiao Cheng go to the farm with us?
8)对方式或程度等提出疑问,用疑问词How。
eg. go by bike like very much
9)对数量提出疑问,疑问词为How many,要注意how many必须跟名词的复数形式。
eg. two hundred sheep→How many sheep
10)对价格提出疑问,疑问词用How much。
eg. I paid fifty yuan for the sweater.
______ ______ did you pay for the sweater?
11)对时间长度提出疑问,疑问词应用How long。
eg. I've worked in that factory for two years. (划线提问)96中考题
______ _____ _______ you worked in that factory?
12)对时间频率,如 once a year, twice a week等提问,疑问词用How often。
13)对具体次数,如 once, twice, three times等提问,疑问词用How many times。
eg. ______ did he call you the day before yesterday?Twice. 96中考题
A.What time B.How many times C.How much D.How long
14)对in+一段时间提问,疑问词一般用How soon。
eg. Jane and her brother will finish the work in two hours. (划线提问)
_____ _____ _____ Jane and her brother finish the work?
15)对距离提出疑问,疑问词用How far。
eg. It's about two kilometres from here to the country.(划线提问)
______ _____ _____ _____ from here to the country?
16)另外,对日期、星期、天气等提出疑问,则分别用
What's the date?
What day is it ? 如果是过去时间,就用was代替is。
What's the weather like?
练习题
1)She does exercises at home in the evening.(改成否定句、一般疑问句)
She ______ ______ exercises at home in the evening.
______ she _____ exercises at home in the evening?
2)He said something important at the meeting.(改为否定句,一般疑问句)
He _____ ______ ______ important at the meeting.
______ he ______ ______ important at the meeting?
3)It'll take them three weeks to finish the work.(划线提问)
______ ______ _______ it take them to finish the work?
4)I he to wash all the plates and things after meals.(划线提问)
_____ _____ you he to wash all the plates and things?
5)The woman in the red coat is her mother.(划线提问)
______ ______ is her mother?
6)Li Ping spent twenty yuan on the dictionary.(划线提问)
_____ ____ ____ Li Ping _____ on the dictionary?
思考题
1)The worker's visited the factory already.(改成否定句、一般疑问句)
The worker _____ _____ the factory ______.
____ the worker ___ the factory __?
2)Both of his parents are workers.(改成否定句)
___ of his parents ______ a worker.
3)He went to the park with his sister.(划线提问)
_____ ____ ____ he go to the park?
4)We really enjoyed working on the farm.(划线提问)
What _____ you really enjoy ______?
5)She writes to her parents once a week.(划线提问)
_______ ______ ______ she write to her parents?
6)Our P.E teacher has been at this school since he came.(划线提问)
______ ______ ______ our P.E teacher been at this school?
一、陈述句:是用来陈述一件事情或表示一种看法,可分为肯定句和否定句两种形式。
1、谓语动词是be动词,助动词he, has, will,情态动词can等时,只要直接在这些词后面加not就构成否定形式。
eg. Lily has already read this new book. (改为否定句)
Lily ______ ______ this new book ________.
2、谓语动词是行为动词而又没有助动词或情态动词时,必须在谓语动词前加助动词,一般现在时加助动词do ,第三人称单数加does,一般过去时加did,再和not构成否定结构。必须指出的是:don't, doesn't, didn't后都用动词原形。
eg.1)Jill has lunch at school every day. (改为否定句)
Jill _____ _____ lunch at school every day.
2)The children had a good time at the party. (改为否定句)
The children ______ _____ a good time at the party.
3)Rose didn't drink any milk this morning.(改为肯定句)
Rose ______ ______ milk this morning.
二、疑问句:是用来提出问题的句子。
A.一般疑问句:以be动词, he /has/do等助动词、can/may等情态动词开头,以yes或no来回答的问句。
它的基本结构是:Be/He /Has/Did等助动词(包括情态动词)+主语+谓语(包括表语)+┄?回答常用简略回答。
1、谓语动词是be动词、助动词、情态动词时,只要直接把这些词置于句首,句末改成问号。
eg. There's something wrong with his bike.(改成疑问句)
______ _____ _______ wrong with his bike?
2、谓语动词是行为动词时,必须在句首加上助动词Do、Does(三单)、Did(过去式)加上这些助动词后,句子中谓语动词必须用原形。
eg. 1)Edison built a science lab himself when he was ten. (改成疑问句)
______ Edison ______ a science lab himself when he was ten?
2)Those Japanese like Chinese food.(改成疑问句)
______ those Japanese ________ Chinese food?
注意:在把肯定句改成否定句或一般疑问句的时候,要注意句中是否有already、some、something、somebody等词,如果有也必须进行改变,already要改成yet,some、something、somebody等分别改成any、anything、anybody等。另外,在改成否定句的时候注意把too改成either,both改成neither,all改成none等.在改成一般疑问句的时候,常常把第一人称I、we改成第二人称you。
B.特殊疑问句:以疑问代词或疑问副词开头,提出疑问的句子。
它的基本结构是:特殊疑问词+一般疑问句语序。但是如果疑问词在句子中作主语或作主语的定语,就用特殊疑问词+陈述句语序。常用的疑问词有:what, who(whom), whose,which,when,where,how,why等,回答时针对问句中的代词和副词来回答,不用yes或no来回答。
1)对指物名词或谓语动词提出疑问,疑问词用what
①The twins were making a kite when their mother came in. (划线提问)
______ _____ the twins _____ when their mother came in?
②Mrs Turner asked her son to buy some eggs for supper. (划线提问)
_______ ______ Mrs Turner ask her son ______ _______?
2)对名词前定语提出疑问,疑问词应用which,而且必须和名词连用。
I'm going to take the shirt on the right.(划线提问)
______ _____ are you going to take?
3)对指人名词或代词提问用who,作宾语时提问用whom。
eg.Li Ping,they,his father
4)对物主代词和名词所有格提问用whose。
eg. Li Ping's coat→Whose coat my father→Whose father
5)对具体时间提出疑问,如 in the morning,last Sunday等,疑问词用when;对具体几点钟提问,疑问词应用what time。
6)对具体地点提出疑问,疑问词应用where。
The pupils are hing a picnic at the foot of the hill. (划线提问)
_____ _____ the pupils hing a picnic?
7)对表原因的从句提问,常见的有because引导的从句,疑问词应用why。
Xiao Cheng didn't go to the farm with us because he was ill. (划线提问)
_______ _____ Xiao Cheng go to the farm with us?
8)对方式或程度等提出疑问,用疑问词How。
eg. go by bike like very much
9)对数量提出疑问,疑问词为How many,要注意how many必须跟名词的复数形式。
eg. two hundred sheep→How many sheep
10)对价格提出疑问,疑问词用How much。
eg. I paid fifty yuan for the sweater.
______ ______ did you pay for the sweater?
11)对时间长度提出疑问,疑问词应用How long。
eg. I've worked in that factory for two years. (划线提问)96中考题
______ _____ _______ you worked in that factory?
12)对时间频率,如 once a year, twice a week等提问,疑问词用How often。
13)对具体次数,如 once, twice, three times等提问,疑问词用How many times。
eg. ______ did he call you the day before yesterday?Twice. 96中考题
A.What time B.How many times C.How much D.How long
14)对in+一段时间提问,疑问词一般用How soon。
eg. Jane and her brother will finish the work in two hours. (划线提问)
_____ _____ _____ Jane and her brother finish the work?
15)对距离提出疑问,疑问词用How far。
eg. It's about two kilometres from here to the country.(划线提问)
______ _____ _____ _____ from here to the country?
16)另外,对日期、星期、天气等提出疑问,则分别用
What's the date?
What day is it ? 如果是过去时间,就用was代替is。
What's the weather like?
练习题
1)She does exercises at home in the evening.(改成否定句、一般疑问句)
She ______ ______ exercises at home in the evening.
______ she _____ exercises at home in the evening?
2)He said something important at the meeting.(改为否定句,一般疑问句)
He _____ ______ ______ important at the meeting.
______ he ______ ______ important at the meeting?
3)It'll take them three weeks to finish the work.(划线提问)
______ ______ _______ it take them to finish the work?
4)I he to wash all the plates and things after meals.(划线提问)
_____ _____ you he to wash all the plates and things?
5)The woman in the red coat is her mother.(划线提问)
______ ______ is her mother?
6)Li Ping spent twenty yuan on the dictionary.(划线提问)
_____ ____ ____ Li Ping _____ on the dictionary?
思考题
1)The worker's visited the factory already.(改成否定句、一般疑问句)
The worker _____ _____ the factory ______.
____ the worker ___ the factory __?
2)Both of his parents are workers.(改成否定句)
___ of his parents ______ a worker.
3)He went to the park with his sister.(划线提问)
_____ ____ ____ he go to the park?
4)We really enjoyed working on the farm.(划线提问)
What _____ you really enjoy ______?
5)She writes to her parents once a week.(划线提问)
_______ ______ ______ she write to her parents?
6)Our P.E teacher has been at this school since he came.(划线提问)
______ ______ ______ our P.E teacher been at this school?
句型转换题是中考常见题型,它主要用来考查大家对句子结构的构成、变化的掌握及在行文中的运用等,类型繁多。现以近两年中考题为例,分类介绍如下:
[第一类] 改成否定句
英语中有关否定的结构各不相同,除动词部分构成的否定外,还有名词、代词的否定、部分否定、否定转移、以及一些表示否定意义的短语或句型等。
一、含有连系动词、情态动词等助动词的句子改为否定句时,在连系动词、情态动词等的后面加not就行了。如:(划线部分为正确答案,下同。)
1. He was late for school yesterday. (2005黑龙江省泰州市)
He wasn’t late for school yesterday.
2. The students of No.2 Middle School he gone for a picnic already. (2004新疆)
The students of No.2 Middle School hen’t gone for a picnic yet.
二、祈使句变否定句一般在其前加don’t。如:
3. Open the window. (2005江苏省)
Don’t open the window.
三、实义动词的否定式是在实义动词前加don’t, doesn’t, didn’t等。如:
4. She does the housework every day. (2005黑龙江省哈尔滨市)
She doesn’t do the housework every day.
5. He returned the book to the library this morning. (2004重庆市)
He didn’t return the book to the library this morning.
注意:变否定句时须注意某些词语的变化,如some改为any, something改为anything, already改为yet, both改为neither, all改为none等。又如:
6. Both of them are my best friends. (2004甘肃省兰州市)
Neither of them is my best friend.
[第二类] 改为疑问句
可分为一般疑问句、选择疑问句和反意疑问句。
一、变一般疑问句时,含有连系动词、情态动词的句子,只需将它们移至句首,第一个字母变为大写,句尾改为问号即可。含有实义动词的句子,在实义动词前加do, does, did等。变化过程中也要注意某些词语和人称的变化。如:
7. There’s something to eat in the cupboard.(2005贵州省贵阳市)
Is there anything to eat in the cupboard?
8. Kate does morning exercises every day. (2004山东省济南市)
Does Kate do morning exercises every day?
9. Ann returned the book to the library yesterday. (2005四川省成都市)
Did Ann return the book to the library yesterday?
二、变选择疑问句时,如果该句是一般疑问句,则在后面直接加“or+另一选择部分”就行了;若是陈述句,则要先变成一般疑问句。如:
10. John is an American. (用a Canadian改为选择疑问句)(2004新疆)
Is John an American or a Canadian?
三、变反意疑问句时,要注意“前肯后否”和“前否后肯”,还要注意一些特殊形式的反意疑问句。如:
11. She has hardly had anything this morning, has she?(2005山东省泰安市)
12. You will meet your friends at the railway station, won’t you?(2004重庆)
13. She had nothing for breakfast, did she?(2005青海)
14. There was no time for the twins to go shopping, was there?(2004黑龙江省哈尔滨市)
英语八大时态的句式结构和用法
一、How are you doing? 你好吗?
美国人见面时候常用的打招呼方式就是:"Hey! How are you doing?" 或是 "How are you?" 不然 "How's going?" 也很常见。我觉得这种每天跟别人打招呼的习惯,就是跟美国友人建立良好关系的开始。
二、 What's up? 什么事?
"What's up?" 也是很常用的一种打招呼方式。比方说 Bob 在路上看到我跟我说 "Hey! Ann!" 那我通常就会答说 "Hi! Bob. What's up?" 这就是问对方"近来怎样,有什么事吗?”通常如果没什么事人家就会说 "Not much." 感觉上有点像Hello的味道了。
"What's up?" 也常被用来问人家“有什么事?”例如有人登门拜访,你就会说 "What's up? (到底有何贵干啊?)" 总之 "What's up?" 在美国应用的很广,各位一定要熟记才是。
三、Could you do me a for? 能不能帮我一个忙?
人是不能独自一个人活的,需要别人帮忙的地方总是很多,所以我就会常讲 "Could you do me a for?" 或是 "Could you give me a hand?" 这算是比较正式礼貌的讲法。有时候要请别人帮忙但还不太好意思开口,我就会说"Could you do me a little for? (能不能帮我一个小忙?)"其实也许是帮大忙但也要先讲成小忙,先让对方点头才是。 (注意一下这里用 could you 会比 can you 来的客气一点。)
英语的句子类型有哪几种?
1、一般现在时:主语+do/does;用于经常性或习惯性的动作,常与表示频度的时间状语连用。
2、一般过去时:主语+did;用于在确定的过去时间里所发生的动作或存在的状态。
3、一般将来时:will do/;用于表示主观意愿的将来、不以人的意志为转移的客观的将来、临时决定,通常用于对话中。
4、现在进行时:主语+am/is/are doing;用于表示现在(指说话人说话时)正在发生的事情。
5、过去进行时:was/were doing;用于表示过去某段时间内持续进行的动作或者事情。
6、过去将来时:was/were to /would do;用于表示主观意愿的将来。
7、现在完成时:he/has done;用于表示刚刚完成的事情或活动作。
8、过去完成时:had done。用于表示在过去不同时间发生的两个动作中,发生在先,用过去完成时,发生在后,用一般过去时。
英语中的八个基本时态,即:一般现在时、一般过去时、一般将来时、过去将来时、现在进行时、过去进行时、现在完成时、过去完成时。
英文的8种时态归纳:
1. 一般现在时
①定义;表示经常性的事情,经常性的动作或一般实。
②时间状语:often,usually,always,every,sometimes,at等等。
③结构:只有在第三人称单数用动词的“三单变化”,其他用动词的原形。
④否定形式:am/is/are+not;此时态的谓语动词若为行为动词,则在其前加don't,如主语为第三人称单数,则用doesn't,同时还原行为动词。
⑤句子转换:当转换成一般疑问句时,把be动词放于句首,用助动词提问,并根据是否为第三人称单数而改动,后面的动词也要改为原形。
2. 一般过去时
①定义:表示过去某一时候或某一段时间所发生了的事情或存在的状态。
②时间状语:yesterday, this morning, just now, a moment ago, in May, last night / year / week, once upon a time, the other day, before等等。
③结构:be动词
④否定形式:was/were+not;在行为动词前加didn't,同时还原行为动词。
⑤句子转换:当转换成一般疑问句时,was或were放于句首;用助动词do的过去式did 提问,同时还原行为动词。
3. 现在进行时
①定义:表示说话时正在进行或发生的动作,也可表示当前一段时间内的活动或现阶段正在进行的动作。
②时间状语:now,at this moment,these days等等。
③结构:助动词 be ( am / is / are ) +doing。
④否定形式:be ( am / is / are ) +not +doing。
⑤句子转换:当转换成一般疑问句时,把be动词放于句首。
4. 过去进行时
①定义:表示在过去某个时间点发生或进行的行为的事情。
②时间状语:at this time yesterday, at that time或以when引导的谓语动词等等。
③结构:be (was/were )+doing。
④否定形式:be (was/were )+not+doing。
⑤句子转换:当转换成一般疑问句时,把be动词放于句首。
5. 现在完成时
①定义:表示过去发生的动作对现在造成的影响或结果或过去的动作或状态持续到现在。
②时间状语:recently, lately, since…for…,in the past few years等等。
③结构:主语+he/has +动词的过去分词。
④否定形式:主语+he/has + not +动词的过去分词。
⑤句子转换:当转换成一般疑问句时,把he/has放于句首。
6. 过去完成时
①定义:表示在过去某一时刻或动作以前完成了的动作,也可以说过去的时间关于过去的动作。即“过去的过去”。
②时间状语:by, before等介词短语。
③结构:主语+had+过去分词。
④否定形式:主语+had+ not +过去分词。
⑤句子转换:当转换成一般疑问句时,had放于句首。
7. 一般将来时
①定义:表示将来某一时刻的动作或状态,或将来某一段时间内经常的动作或状态。
②时间状语:tomorrow,next day,soon,in a few minutes,soon, by
③结构:be ( am / is / are ) going to+动词原形,shall/will+动词原形。
④否定形式:be ( am / is / are ) not going to+动词原形,shall/will not+动词原形。
⑤句子转换:当转换成一般疑问句时,把be动词/shall/will放于句首。
8. 过去将来时
①定义:表示在过去某个时间看来将要发生的动作或存在的状态。
②时间状语:the next day,the following month等等。
③结构:would/should+动词原形,be(was,were)going to+动词原形。
④否定形式:would/should not+动词原形,be(was,were)not going to+动词原形。
⑤句子转换:当转换成一般疑问句时,把be动词/would/should放于句首。
平常常见(常用)的英语句子有哪些?
一般有简单句、复合句、并列句。
复合句:也就是简单句的某个成分变成丛句了。
是由主句+从句构成,它是英语中比较复杂的句子结构。一般来说,英语中一个句子只能有一个谓语,如果出现两个谓语动词,那么其中一个谓语动词只能以从句的形式或并列句或非谓语动词的形式出现。所谓从句是指从属于主句的句子,由从属连词连接。从句的种类有很多,但根据其性质和作用可以分为:名词性从句,形容词性从句(即定语从句),副词性从句(即状语从句)三大类
并列句
:也就是几个简单句或复合句搞在一起
由连接词或
"
"把两个以上(含两个)的简单句连在一起的句子叫做并列句。在并列句中,各个简单句意思完整,不受其他简单句的影响。
These
flowers
are
white
and
those
flowers
are
red。
这些花是白色的而那些花是红色的。
1.
简单句的五种形式:
(1)主语+谓语(不及物动词);
(2)主语+谓语(及物动词)+宾语;
(3)主语+谓语+宾语+补语;
(4)主语+谓语+间接宾语+直接宾语;
(5)主语+系动词+表语。
两类系动词:①be动词;
②一些实义动词用作系动词:feel,
taste,
smell等;
2.
并列句:一个句子当中包含两个或更多互不相依存的主谓结构,中间用一些连接词连接起来的句子。
并列句不能只用逗号隔开,而要用连接词连接。
简单句和并列句是复合句的基础。
英语基本句型有哪些
1. I see. 我明白了.
2. I quit! 我不干了!
3. Let go! 放手!
4. Me too. 我也是.
5. My god! 天哪!
6. No way! 不行!
7. Come on. 来吧(赶快)
8. Hold on. 等一等.
9. I agree. 我同意.
10. Not bad. 还不错.
11. Not yet. 还没.
12. See you. 再见.
13. Shut up! 闭嘴!
14. So long. 再见.
15. Why not? 好呀! (为什么不呢?)
16. Allow me. 让我来.
17. Be quiet! 安静点!
18. Cheer up! 振作起来!
19. Good job! 做得好!
20. He fun! 玩得开心!
21. How much? 多少钱?
22. I'm full. 我饱了.
23. I'm home. 我回来了.
24. I'm lost. 我迷路了.
25. My treat. 我请客.
26. So do I. 我也一样.
27. This way. 这边请.
28. After you. 您先.
29. Bless you! 祝福你!
30. Follow me. 跟我来.
31. Forget it! 休想! (算了!)
32. Good luck! 祝好运!
33. I decline! 我拒绝!
34. I promise. 我保证.
35. Of course! 当然了!
36. Slow down! 慢点!
37. Take care! 保重!
38. They hurt. (伤口)疼.
39. Try again. 再试试.
40. Watch out! 当心.
41. What's up? 有什么事吗?
42. Be careful! 注意!
43. Bottoms up! 干杯(见底)!
44. Don't move! 不许动!
45. Guess what? 猜猜看?
46. I dou it 我怀疑.
47. I think so. 我也这么想.
48. I'm single. 我是单身贵族.
49. Keep it up! 坚持下去!
50. Let me see.让我想想.
51. Never mind.不要紧.
52. No problem! 没问题!
53. That's all! 就这样!
54. Time is up. 时间快到了.
55. What's new? 有什么新鲜事吗?
56. Count me on 算上我.
57. Don't worry. 别担心.
58. Feel better? 好点了吗?
59. I love you! 我爱你!
60. I'm his fan. 我是他的影迷.
61. Is it yours? 这是你的吗?
62. That's neat. 这很好.
63. Are you sure? 你肯定吗?
64. Do l he to 非做不可吗?
65. He is my age. 他和我同岁.
66. Here you are. 给你.
67. No one knows . 没有人知道.
68. Take it easy. 别紧张.
69. What a pity! 太遗憾了!
70. Any thing else? 还要别的吗?
71. To be careful! 一定要小心!
72. Do me a for? 帮个忙,好吗?
73. Help yourself. 别客气.
74. I'm on a diet. 我在节食.
75. Keep in Touch. 保持联络.
76. Time is money. 时间就是金钱.
77. Who's calling? 是哪一位?
78. You did right. 你做得对.
79. You set me up! 你出卖我!
80. Can I help you? 我能帮你吗?
81. Enjoy yourself! 祝你玩得开心!
82. Excuse me,Sir. 先生,对不起.
83. Give me a hand! 帮帮我!
84. How's it going? 怎么样?
85. I he no idea. 我没有头绪.
86. I just made it! 我做到了!
87. I'll see to it 我会留意的.
88. I'm in a hurry! 我在赶时间!
89. It's her field. 这是她的本行.
90. It's up to you. 由你决定.
91. Just wonderful! 简直太棒了!
92. What about you? 你呢?
93. You owe me one.你欠我一个人情.
94. You're welcome. 不客气.
95. Any day will do. 哪一天都行夕
96. Are you kidding? 你在开玩笑吧!
. Congratulations! 祝贺你!
98. T can't help it. 我情不自禁.
99. I don't mean it. 我不是故意的.
100. I'll fix you Up. 我会帮你打点的
101. It sounds great!. 听起来很不错.
102. It's a fine day. 今天是个好天.
103. So far,So good. 目前还不错.
104. What time is it? 几点了?
105. You can make it! 你能做到!
106. Control yourself! 克制一下!
107. He came by train. 他乘火车来.
108. He is ill in bed. 他卧病在床.
109. He lacks courage. 他缺乏勇气.
110. How's everything? 一切还好吧?
111. I he no choice. 我别无选择.
112. I like ice-cream. 我喜欢吃冰淇淋.
113. I love this game. 我钟爱这项运动.
114. I'll try my best. 我尽力而为.
115. I'm On your side. 我全力支持你.
116. Long time no see! 好久不见!
117. No pain,no gain. 不劳无获.
118. Well,it depends 噢,这得看情况.
119. We're all for it. 我们全都同意.
120. What a good deal! 真便宜!
121. What should I do? 我该怎么办?
122. You asked for it! 你自讨苦吃!
123. You he my word. 我保证.
124. Believe it or not! 信不信由你!
125. Don't count on me.别指望我.
126. Don't fall for it! 别上当!
127. Don't let me down. 别让我失望.
128. Easy come easy go. 来得容易,去得快.
129. I beg your pardon. 请你原谅.
130. I beg your pardon? 请您再说一遍(我没有听清).
131. I'll be back soon. 我马上回来.
132. I'll check it out. 我去查查看.
133. It’s a long story. 说来话长.
134. It’s Sunday today. 今天是星期天.
135. Just wait and see! 等着瞧!
136. Make up your mind. 做个决定吧.
137. That's all I need. 我就要这些.
138. The view is great. 景色多么漂亮!
139. The wall has ears. 隔墙有耳.
140. There comes a bus. 汽车来了.
141. What day is today? 今天星期几?
142. What do you think? 你怎么认为?
143. Who told you that? 谁告诉你的?
144. Who's kicking off? 现在是谁在开球?
145. Yes,I suppose So. 是的,我也这么认为.
146. You can't miss it 你一定能找到的.
147. Any messages for me? 有我的留言吗?
148. Don't be so modest. 别谦虚了.
149. Don't give me that! 少来这套!
150. He is a smart boy. 他是个小机灵鬼.
151. He is just a child. 他只是个孩子.
152. I can't follow you. 我不懂你说的.
153. I felt sort of ill. 我感觉有点不适.
154. I he a good idea! 我有一个好主意.
155. It is growing cool. 天气渐渐凉爽起来.
156. It seems all right. 看来这没问题.
157. It's going too far. 太离谱了.
158. May I use your pen? 我可以用你的笔吗?
159. She had a bad cold. 她患了重感冒.
160. That's a good idea. 这个主意真不错.
161. The answer is zero. 白忙了.
162. What does she like? 她喜欢什么?
163. As soon as possible! 越快越好!
164. He can hardly speak. 他几乎说不出话来.
165. He always talks big. 他总是吹牛.
166. He won an election. 他在选举中获胜.
167. I am a football fan. 我是个足球迷.
168. If only I could fly. 要是我能飞就好了.
169. I'll be right there. 我马上就到.
170. I'll see you at six. 我六点钟见你.
171. IS it true or false? 这是对的还是错的?
172. Just read it for me. 就读给我听好了.
173. Knowledge is power. 知识就是力量.
174. Move out of my way! 让开!
175. Time is r
176. We are good friends. 我们是好朋友.
177. What's your trouble? 你哪儿不舒服?
178. You did fairly well! 你干得相当不错1
179. Clothes make the man. 人要衣装.
180. Did you miss the bus? 你错过公共汽车了?
181. Don't lose your head. 不要惊慌失措.
182. He can't take a joke. 他开不得玩笑.
183. He owes my uncle $100.他欠我叔叔100美元.
184. How are things going? 事情进展得怎样?
185. How are you recently? 最近怎么样?
186. I know all about it. 我知道有关它的一切.
187. It really takes time. 这样太耽误时间了.
188. It's against the law. 这是违法的.
189. Love me,love my dog. (谚语)爱屋及乌.
190. My mouth is watering. 我要流口水了.
191. Speak louder,please. 说话请大声点儿.
192. This boy has no job. 这个男孩没有工作.
193. This house is my own. 这所房子是我自己的.
194. What hened to you? 你怎么了?
195. You are just in time. 你来得正是时候.
196. You need to workout. 你需要去运动锻炼一下.
1. Your hand feels cold. 你的手摸起来很冷.
198. Don't be so childish. 别这么孩子气.
199. Don't trust to chance! 不要碰运气.
英语五种基本句型列式如下:
基本句型一: S V (主+谓)
基本句型二: S V P (主+谓+表)
基本句型三: S V O (主+谓+宾)
基本句型四: S V o O (主+谓+间宾+直宾)
基本句型五: S V O C (主+谓+宾+宾补)
基本句型 一
此句型的句子有一个共同特点,即句子的谓语动词都能表达完整的意思。
这类动词叫做不及物动词,后面可以跟副词、介词短语、状语从句等。
┏━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━┯━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━┓
┃ S │ V (不及物动词) ┃
┠———————————————┼———————————————┨
┃1. The sun │was shining. ┃
┃2. The moon │rose. ┃
┃3. The universe │remains. ┃
┃4. We all │breathe, eat, and drink. ┃
┃5. Who │cares? ┃
┃6. What he said │does not matter. ┃
┃7. They │talked for half an hour. ┃
┃8. The pen │writes smoothly ┃
1. 太阳在照耀着。 2. 月亮升起了。
3. 宇宙长存。 4. 我们大家都呼吸、吃和喝。
5. 管它呢? 6. 他所讲的没有什么关系。
7. 他们谈了半个小时。 8. 这支笔书写流利。
基本句型 二
此句型的句子有一个共同的特点:句子谓语动词都不能表达一个完整的意思,必须加上一个表明主语身份或状态的表语构成复合谓语,才能表达完整的意思。这类动词叫做连系动词。系动词分两类:be, look, keep, seem等属一类,表示情况;get, grow, become, turn等属另一类,表示变化。be 本身没有什么意义,只起连系主语和表语的作用。其它系动词仍保持其部分词义。
┏━━━━━━━┯━━━━━━━┯━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━┓
┃ S │V(是系动词)│ P ┃
┠———————┼———————┼———————————————┨
┃1. This │is │an English-Chinese dictionary.┃
┃2. The dinner │smells │good. ┃
┃3. He │fell │in love. ┃
┃4. Everything │looks │different. ┃
┃5. He │is growing │tall and strong. ┃
┃6. The trouble│is │that they are short of money. ┃
┃7. Our well │has gone │dry. ┃
┃8. His face │turned │red. ┃
┗━━━━━━━┷━━━━━━━┷━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━┛
1. 这是本英汉辞典。 2. 午餐的气味很好。
3. 他堕入了情网。 4. 一切看来都不同了。
5. 他长得又高又壮。 6. 麻烦的是他们缺少钱。
7. 我们的井干枯了。 8. 他的脸红了。
基本句型 三
此句型句子的共同特点是:谓语动词都具有实义,都是主语产生的动作,但不能表达完整的意思,必须跟有一个宾语,即动作的承受者,才能使意思完整。这类动词叫做及物动词。
┏━━━━━━━┯━━━━━━━┯━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━┓
┃ S │V(及物动词)│ O ┃
┠———————┼———————┼———————————————┨
┃1. Who │knows │the answer? ┃
┃2. She │smiled │her thanks. ┃
┃3. He │has refused │to help them. ┃
┃4. He │enjoys │reading. ┃
┃5. They │ate │what was left over. ┃
┃6. He │said │"Good morning." ┃
┃7. I │want │to he a cup of tea. ┃
┃8. He │admits │that he was mistaken. ┃
┗━━━━━━━┷━━━━━━━┷━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━
1. 谁知道答案? 2. 她微笑表示感谢。
3. 他拒绝帮他们的忙。 4. 他喜欢看书。
5. 他们吃了剩饭。 6. 他说:“早上好!”
7. 我想喝杯茶。 8. 他承认犯了错误。
基本句型 四
此句型的句子有一个共同特点:谓语动词必须跟有两个宾语才能表达完整的意思。这两个宾语一个是动作的直接承受者,另一个是动作的间接承受者。
通常这一间接承受者用一个介词来连接,当动作的间接承受者在动作的直接承受者之前时,这一介词往往被省略。
┏━━━━┯━━━━━┯━━━━━━━┯━━━━━━━━━━━━┓
┃ S │V(及物)│ o(多指人) │ O(多指物) ┃
┠————┼—————┼———————┼————————————┨
┃1. She │ordered │herself │a new dress. ┃
┃2. She │cooked │her husband │a delicious meal. ┃
┃3. He │brought │you │a dictionary. ┃
┃4. He │denies │her │nothing. ┃
┃5. I │showed │him │my pictures. ┃
┃6. I │ge │my car │a wash. ┃
┃7. I │told │him │that the bus was late. ┃
┃8. He │showed │me │how to run the machine. ┃
┗━━━━┷━━━━━┷━━━━━━━┷━━━━━━━━━━━━┛
1. 她给自己定了一套新衣裳。 2. 她给丈夫煮了一餐美馔。
3. 他给你带来了一本字典。 4. 他对她什么都不拒绝。
5. 我给他看我的照片。 6. 我洗了我的汽车。
7. 我告诉他汽车晚点了。 8. 他教我开机器。
基本句型 五
此句型的句子的共同特点是:动词虽然是及物动词,但是只跟一个宾语还
不能表达完整的意思,必须加上一个补充成分来补足宾语,才能使意思完整。
┏━━━━┯━━━━━┯━━━━━━━┯━━━━━━━━━━━━┓
┃ S │V(及物)│ O(宾语) │ C(宾补) ┃
┠————┼—————┼———————┼————————————┨
┃1. They │ointed │him │manager. ┃
┃2. They │painted │the door │green. ┃
┃3. This │set │them │thinking. ┃
┃4. They │found │the house │deserted. ┃
┃5. What │makes │him │think so? ┃
┃6. We │saw │him │out. ┃
┃7. He │asked │me │to come back soon. ┃
┃8. I │saw │them │getting on the bus. ┃
┗━━━━┷━━━━━┷━━━━━━━┷━━━━━━━━━━━━┛
1. 他们任命他当经理。 2. 他们把门漆成绿色。
3. 这使得他们要细想一想。 4. 他们发现那房子无人居住。
5. 他怎么会这样想? 6. 我们送他出去。
7. 他要我早点回来。 8. 我看见他们上了那辆公共汽车。
但常用的英语句子并不都象基本句型这样简短,这些句子除了基本句型的
成分不变外,通常是在这些成分的前面或后面增加一些修饰语(modifier)而
加以扩大。这些修饰语可以是单词(主要是形容词、副词和数词),也可以是
各种类型的短语(主要是介词短语、不定式短语和分词短语)。下面以基本句
型五为例:
We found the hall full.
我们发现礼堂坐满了。
We found the great hall full of students and teachers.
我们发现大礼堂坐满了学生和教师。
We found the great hall full of students and teachers listen-
ing to an important report.
我们发现大礼堂坐满了学生和教师,在听一个重要报告。
We found the great hall full of students and teachers listen-
ing to an important report made by a comrade from the People's
Daily on current affairs in East Europe.
我们发现大礼堂坐满了学生和教师,在听人民日报的一位同志作有关
东欧局势的重要报告。
不同的动词使用的句型也不尽一样,因此在学习动词时,应掌握动词的类
型。以 get 为例:
He's getting angry. (S V C)
He got through the window. (S V M)
You'll get a surprise. (S V O)
He got his shoes and socks wet. (S V O C)
He got himself into trouble. (S V O M)
He got her a splendid present. (S V 0 O)
在句子中词类和词的位置也影响句子的句型和意思:
I found the book easily.我很容易地找到了这本书。(S V O M)
I found the book easy. 我觉得这本书很容易。 (S V O C)
I he to do something. 我得做点事。
I he something to do. 我有点事做。