您现在的位置是: 首页 > 搞笑语录 搞笑语录
英语句子结构知识点总结_英语句子结构基础入门
tamoadmin 2024-08-24 人已围观
简介1.初二英语下册知识点:重点短语~句子形式~时态(要一晚可以记下/能拿80分以上的) 急急急急急急急急急2.初中英语宾语从句知识点归纳3.小升初英语语法强调句知识点总结4.关于英语感叹句的知识点 来几个典型句子并总结,谢谢5.谁能帮忙总结一下有关于倒装句的知识,具体如下6.高一英语语法知识点归纳总结7.高中英语语法知识点总结8.全部倒装与部分倒装有什么区别? 想学好外语,有许多事情要做,学校的课业
1.初二英语下册知识点:重点短语~句子形式~时态(要一晚可以记下/能拿80分以上的) 急急急急急急急急急
2.初中英语宾语从句知识点归纳
3.小升初英语语法强调句知识点总结
4.关于英语感叹句的知识点 来几个典型句子并总结,谢谢
5.谁能帮忙总结一下有关于倒装句的知识,具体如下
6.高一英语语法知识点归纳总结
7.高中英语语法知识点总结
8.全部倒装与部分倒装有什么区别?
想学好外语,有许多事情要做,学校的课业负担也很重,如何合理地安排时间呢?在这里有16个字:化整为零,集中歼灭,见缝插针,持之以恒。以下是我给大家整理的 高一英语 下册必记知识点解析,希望大家能够喜欢!
高一英语下册必记知识点解析1
一. 直接引语和间接引语
(一)直接引述别人的原话,叫做直接引语;用自己话转述别人的话,叫做间接引语。间接引语一般构成宾语从句。直接引语必须放在引号内,间接引语则不用引号。直接引语改为间接引语时,除将引语部分变成宾语从句外,还必须对直接引语中的人称、时态、指示代词、时间状语、地点状语等进行改变。
1. 时态的变化:直接引语变为间接引语时,通常受转述动词said, asked等的影响而使用过去化的时态,即把原来的时态向过去推,也就是一般现在时变为一般过去时,现在进行时变为过去进行时,等等。例如:
Tom said to me,“My brother is doing his homework.”
→Tom said to me that his brother was doing his homework.
2. 人称代词、指示代词、时间状语、地点状语等等的变化: 根据意义进行相应的变化,例如:
She asked Jack,“Where he you been?”
→She asked Jack where he had been.
He said,“These books are mine.”
→He said that those books were his.
(二)直接引语改为间接引语时,都使用陈述语序,但是因为原句的句式不同,所以变成间接引语时所用的连词会有所不同。直接引语如果是一般疑问句,用连接词whether或if;如果是特殊疑问句,则用疑问词引导间接引语。转述的动词一般用asked,可以在其后加上一个间接宾语me, him, her, us等。如:
She said,“Is your father at home?”
→She asked me if/whether my father was at home.
“What do you do every Sunday?”My friend asked me.
→My friend asked me what I did every Sunday.
直接引语如果是祈使句,改为间接引语时,要将祈使句的动词原形变为带to的不定式,并在不定式的前面根据原句的语气(即请求或命令)加上ask, tell, order等动词,如果祈使句为否定式,则在不定式前加not。其句型为:ask / tell / order someone (not) to do something. 例如:
She said to us,“Please sit down.”
→She asked us to sit down.
He said to him,“Go away!”
→He ordered him to go away.
He said, “Don’t make so much noise, boys.”
→He told the boys not to make so much noise.
二. 各种时态的被动语态
被动语态概述
被动语态的概念:它是动词的一种形式,表示主语与谓语之间的执行或被执行关系。主动语态表示主语是谓语动作的执行者,例如:They saw the little boy crying by the river. 被动语态表示主语是谓语动作的承受者,例如:The little boy was seen crying by the river.
被动语态的构成
被动语态的形式是由“助动词be+动词的过去分词”构成。助动词be随着主语的人称、数、时态等的不同而变化。几种常见时态的被动语态形式如下:
1. 一般现在时 am/is/are + 过去分词
例如:Rice is planted in the south of China.
2. 一般过去时 was/were + 过去分词
例如:These trees were planted the year before last.
3. 一般将来时 will/shall + be + 过去分词
例如:A sports meeting will be held next week in our school.
4. 现在进行时 am/is/are + being + 过去分词
例如:Your radio is being repaired now.
5. 过去进行时 was/were + being + 过去分词
When he got there, the problem was being discussed.
6. 现在完成时 he/has + been + 过去分词
His work has been finished.
Has his work been finished? Yes, it has. / No, it hasn’t.
7. 过去完成时 had + been + 过去分词
注意:
1.除了be之外的 其它 系动词如get, stay等也可以和过去分词构成被动语态。例如:Their questions hen’t got answered.
2. 含有情态动词的谓语变成被动语态使用“情态动词+ be + 过去分词”结构。例如:
More attention should be paid to the old in this country.
This work can’t be done until Mr. Black comes.
3. 含有“be going to”, “be to”等结构的谓语,其被动语态分别用“be going to + be + 过去分词”和“be to + be + 过去分词”。例如:
The problem is going to be discussed at the next meeting.
All these books are to be taken to the library.
4. 被动语态与系表结构的区别:“连系动词+用作表语的过去分词”构成的系表结构,与被动语态的形式完全一样,所以应注意它们的区别。被动语态中的过去分词是动词,多强调动作;系表结构中的过去分词相当于形容词,多强调状态。前者通常可用by 引出动作的执行者,而后者则不可以。例如:
The map was changed by someone.(被动结构)
That custom remained unchanged for many centuries.(系表结构)
系表结构中的过去分词通常可被very修饰,被动语态中的过去分词往往要用much修饰。
例如:
He was very excited.(系表结构)
He was much excited by her words.(被动结构)
5. 主动形式表被动意义。有些动词的主动形式有被动意味,如 open, read, sell, shut, wash, wear, write等。此时 句子 的主语一般是物。例如:
These books sell well. 这些书很畅销。
The door won’t shut. 这门关不上。
The clothes wash well. 这些衣服很好洗。
高一英语下册必记知识点解析2
一、一般过去将来时
1.概念:立足于过去某一时刻,从过去看将来,常用于宾语从句中。
2.时间状语:The next day (morning, year…),the following month(week…),etc.
3.基本结构:主语+was/were +going to + do+其它;主语+would/should + do+其它
4.否定形式:主语+was/were+not + going to + do; 主语+would/should + not + do.
5.一般疑问句:was或were放于句首;would/should 提到句首。
6.例句:He said he would go to Beijing the next day.他说他第二天要去北京。
I asked who was going there.我问,谁要去那里。
二、 现在进行时
1.概念:表示现阶段或说话时正在进行的动作及行为。
2.时间状语:Now, at this time, days, etc. look. listen
3.基本结构:主语+be +doing +其它
4.否定形式:主语+be +not +doing+其它
5.一般疑问句:把be动词放于句首。
6.例句:How are you feeling today?你今天感觉如何?
He is doing well in his lessons.在课上他表现得很好。
高一英语下册必记知识点解析3
1. devotes… to doing奉于
2. fight against 对抗,反对,与……作斗争
3. selflessly 无私地
4. be free from 免于,不受
5. be in prison 入狱,在狱中
6. the first man to do 第一个…的人
7. The time when I first met him was a very difficult period of my life.
第一次见到他的时候是在我一生中非常艰难的时期。
8. He was generous with his time, for which I was grateful.
他十分慷慨地给予我时间,我为此非常感激。
9. become out of work. 失业
10. hope that…/to do
11. as soon as I could 尽快, 马上
12. We were put into a position in which we had either to accept we were less important, or fight the .
我们被置于这样一个境地:要么我们被迫接受低人一等的现实,要么跟作斗争。
13. Only 位于句首,修饰状语从句时,主句用部分倒装的语序。
Only in this way can you come up with a solution to the problem.
只有这样,你才能想出解决这个问题的办法。
14. as a matter of fact 事实上
15. blow up 爆炸,打气
16. be equal to 和…平等
17. in trouble 处于困境 遇到麻烦
18. be willing to do sth. 愿意,乐于
19. turn to 变成;求助于,借助于, 翻到,转向
turn to sb for help 向某人求助
20. lose heart 灰心;泄气, 丧失勇气,失去信心
21. escape from 逃脱,逃离,从……逃出
22. should he done 本应做而未做
needn’t he done 本不需要做而做了
can’t he done 过去不可能做过(对过去的否定推测)
must he done 对过去的肯定推测
23. pass the exam. 通过考试
24. be better educated 受到良好 教育
25. come to power 执政
26. be proud to do sth. be proud of sth 为…而自豪
27. set up 创立,建立,架起,建造
The company was set up ten years ago. 公司是十年前建立的。
28. be sentenced to … 被判处……
29. Do you he any thoughts on that 你认为那怎么样?
30. to my understanding 按我的理解 to my opinion
31. be accepted by … 被……录取、接受
32. die from 死于…(事故等外部原因) die of 死于… (疾病等自身原因)
33. under way 正在进行
34. point of view 观点
35. compete with… 与……竞争
36. advise v.
advise + n./pron. advise + doing advise sb. to do sth.
advise + that从句(从句的谓语用“should + v原”, should 常省略)
注:与advise用法类似的动词如forbid,allow,permit,admit,consider等直接接动词作宾语时要用动名词,但接宾补时后跟不定式。
如:We forbid smoking here.
We forbid you to smoke here.
高一英语下册必记知识点解析相关 文章 :
★ 高一英语下册知识点归纳总结
★ 高一下册英语知识点
★ 高一英语必修一知识点汇总笔记
★ 高一英语必修知识点总结
★ 高一英语必修一知识点归纳总结
★ 高一英语必修一重要知识点总结笔记
★ 高一英语必背知识点
★ 人教版高一英语知识点总结
★ 高一英语60个必考知识点
★ 高一英语必修一知识点梳理
初二英语下册知识点:重点短语~句子形式~时态(要一晚可以记下/能拿80分以上的) 急急急急急急急急急
教育 要使人愉快,要让一切的教育带有乐趣。海阔凭你跃,天高任你飞。愿你信心满满,尽展聪明才智;妙笔生花,谱下锦绣第几篇。学习的敌人是自己的知足,要使自己学一点东西,必需从不自满开始。接下来是我为大家整理的 四年级英语 语法知识点汇总,希望大家喜欢!
四年级英语语法知识点汇总一
一、现在进行时的构成
现在进行时由“be+现在分词(v-ing)”构成。be应为助动词,一定不要漏掉哟!它应与主语的人称和数保持一致,即:I am/he/she/it 包括单数名词和不可数名词用is,you/we/they 包括复数名词用are. .现在分词变化规则如下:
1.动词后直接+ ing(例:sleep+ing sleeping)
2.去掉不发音的e+ing(例:bite-e+ing biting)
3.重读闭音节,且末尾只有1个辅音字母,双写辅音字母+ing(例:sitting, beginning,getting,putting,running,stopping,cutting )
4.特殊变化:die-dying,lie-lying,tie-tying
句式构成如下:
肯定句式:主语+be( am,is,are)+现在分词+ 其它 。
否定句式:主语+be(am,is,are)+not +现在分词+其它。
一般疑问句:Be(am,is,are)+主语+现在分词+其它? ,,
特殊疑问句:疑问词+be(am,is,are)+主语+现在分词+其它?
二、现在进行时的应用
A表示现在( 指说话人说话时)正在发生的事情。
例:We are waiting for you.
B. 习惯进行:表示长期的或重复性的动作,说话时动作未必正在进行。
例:Mr. Green is writing another novel.
(说话时并未在写,只处于写作的状态。)
例:She is learning piano under Mr. Smith.
C.已经确定或安排好的将来活动。
I'm leing for a trek in Nepal next week.(已经安排了)
we're flying to Paris tomorrow.(票已经拿到了)
在实际运用时,现在进行时常用以下几种情况:
(1)当 句子 中有now时,常表示动作正在进行,这时要用现在进行时。如:
They are playing basketball now.现在他们正在打 篮球 。
(2)以look, listen开头的句子,提示我们动作正进行,这时要用现在进行时。如:
Listen!She is singing an English song.听,她正在唱英语歌。
(3)表示当前一段时间或现阶段正在进行的动作,且此时有this week, these days等时间状语,这时常用现在进行时。如:
We are making model planes these days.这些天我们在做飞机模型。
(4)描述中的人物的动作,也为了表达更生动。此时也常用现在进行时。如:
Look at the picture. The children are flying kites in the park.看这幅图,那些孩子正在公园放风筝。
四年级英语语法知识点汇总二
语法知识点(一)
一般疑问句以及它的回答。这里涉及的是以系动词开头的问句,例如:她在厨房吗?回答有两种形式:是的,她在。或者 不,她不在。
句子的结构
Is/am/are+主语+表语
例句:Is she in the room?她在房间吗?
回答:Yes, she is./No, she isn't.是的,她在。/不,她不在。
注意:如果用are提问,后面跟的主语是复数,例如他们。
一般疑问句如果用is提问,回答也用is.也就是说用什么提问就一定用什么回答。
语法知识点(二)
特指某人或某物具体在某个地方要用the
例如:他们在书房吗?此时这个书房不是泛指的书房而是特定某个书房的,所以书房前加the。
四年级英语语法知识点汇总三
名词规则变化
名词是表示人或事物名称的词。它既可以表示具体的东西,也可以是表示抽象的东西。
规则变化
1)一般情况下加-s
如book--books(书) desk--desks(书桌)
2)以s ,x ,ch , sh结尾加-es
如box--boxes(盒子) bus--buses(公共汽车)
注意①以 th 结尾加-s, month--months
②stomach--stomachs
3)以辅音字母+结尾,变y为i再加- es。
如city--cities(城市) country--countries(国家)
注意以元音+y,直接加s。如:day--days(天),boy--boys(男孩)
4)以f或fe结尾,复数变f或 fe 为v再加-es
如knife-knives(书) , half-halves(一半)
(thief ,wife ,life ,shelf ,knife ,leaf ,self ,half ,wolf)
注意①有少数词后直接加s,如roof-roofs (屋顶)
5)以o结尾
(1)辅音字母加o结尾名词的加-es
如tomato-tomatoes(西红杮)
potato-potatoes(土豆)
(2) 元音字母加o结尾名词的加-s
如piano-pianos (钢琴), zoo-zoos(动物园)
photo-photos (照片), kangaroo-kangaroos(袋鼠)
kilo-kilos(千克)
注意zero 两种方式都可:zero-zeros或 zeroes(零)
名词不规则变化
名词是表示人或事物名称的词。它既可以表示具体的东西,也可以是表示抽象的东西。
不规则变化
1) 元音字母发变化。
如man--men(男人) , woman--women(妇女)
tooth--teeth(牙齿) , foot--feet(脚)
mouse--mice(老鼠) , policeman--policemen(警察)
policewoman--policewomen(女警察)
2) 词尾发生变化。
如child--children(小孩) , ox--oxen(公牛)
3) 单、复数形式相同。
如fish--fish(鱼) ,sheep--sheep(绵羊) ,deer--deer(鹿) ,chinese--chinese(中国人) ,yuan--yuan(元) ,jinn--jinn(斤)
注意 不说an english,要说an englishman.
①fish作鱼肉讲时不可数,没有复数。
②fishes指各种不同种类鱼或指几条鱼。
4) 形似单数,实为复数意义。
如people(人,人们)these people
(不说a people,可说a person)
police(公安,警察)ten police
(不说a police,可说a policeman)
5) 由man和woman构成的合成名词,变复数将名词及man或woman都变成复数。
如a man driver-men drivers(男司机)
a woman doctor-women doctors (女医生)
6) 合成名词变为复数时,通常只将里面所含的主体名词变为复数。
如passer-by-passers-by(过路人)
bus driver-bus drivers(汽车司机)
注意如果没有主体名词,就在最后一词上加-s。如:
grown-up-grown-ups(成年人)
letter-box-letter-boxes (信箱)
注意①hair和fruit通常作单数,表示总体。若表示若干根头发或若干种水果,则需用这两个词的复数形式。
如would you like some more fruit? 你要不要再吃点水果?
we bought a lot of fruit from the market. 我们从市场上买了许多水果,
china has some good frits. 中国有一些好的水果。(指种类)
she has a few white hairs. 她有几要白头发。
his black hair is going white. 他的黑发逐渐变成灰白色。
注意②wind ,snow和rain这类词,有时也可以有复数形式,表示多次的风、雪或雨。
注意以boy 和girl开头的复合名词变成复数时,一般只把后一名词变成复数。
如 boy student-boy students(男学生)
girlfriend--girlfriends(女朋友)
7) 有些名词只有作复数。
如scissors(剪刀)a pair of scissors(一把剪刀)trousers(裤子)shorts(短裤)jeans(工装裤)compasses(两脚规)scales(天平)sunglasses(太阳镜)surroundings(环境)sings(储蓄)writings(作品)
名词+man(woman)构成的复合名词,其复数形式通常与简单名词一样,即把man(woman)改成men(women)。
如englishman--englishmen(英国人)
frenchwoman--frenchwomen(法国妇女)
注意german不是复合词,它的复数是germans。
初中英语宾语从句知识点归纳
Unit 1 Will people he robots?(自己努力一下,我能帮的已经帮了)
重点语法:一般将来时态的应用
do/does 的一般将来时态形式:(shall/will) do
do/does 的一般将来时态的被动语态:(shall/will) be done
一般将来时态的肯定句、否定句、疑问句形式:
肯定句例句:People will he robots in a few years.
否定句例句:People (will not/won't) he robots in a few years.
一般疑问句例句:Will people he robots in a few years?
特殊疑问句例句:What will people he in a few years?
重点短语:won't = will not
they'll = they will
she'll = she will
he'll = he will
I'll = I will
fall in love with(sb./sth.) 爱上(某人/某物)
be able to do sth. 能够做某事
come true 实现
in the future 未来
hundreds of 数以百计的
thousands of 数以千计的
look for(sb./sth.) 寻找(某人/某物)
will → would 情态动词 will 的原形和过去式
may → might 情态动词 may 的原形和过去式
Reading Strategy(阅读方法)
Look at the title and picture, and predict what you will read about. (看着标题和,预知你要阅读那些方面的内容。)This helps you get ready to acquire new information. (这样可以帮助你获得一些新的信息。)
Unit 2 What should I do?
重点语法:过去将来时态(将来时态的委婉说法)
do/does 的过去将来时态形式:(should/would) do
do/does 的过去将来时态的被动语态:(should/would) be done
过去将来时态的肯定句、否定句、疑问句形式:
肯定句例句:You should write a letter to him.
否定句例句:You shouldn't write a letter to him.
一般疑问句例句:Should I write a letter to him?
特殊疑问句例句:What should I do?
重点短语:keep sb. out 不让某人进入
What's wrong? = What's the matter? = What's the problem? 怎么了?
out of style 不时髦的;过时的
call sb. up 给某人打电话
pay for sth. 为某事付款
part-time job 兼职工作
the same as = be same (to/with) 与……同样
in style 时髦的;流行的
get on [well] with sb. = get along [well] with sb. 与某人相处(好)
didn't = did not
couldn't = could not
as ... as possible 尽可能……(eg/ as soon as possible 尽快)
all kinds of 各种;许多
on the one hand 一方面
on the other hand 另一方面
ask sb. for sth. = ask sb. to do sth. 请求某人做某事
ask sb. not to do sth. 请求某人不要做某事
spend (money) on sth. = spend (money) [in] doing sth. 花钱做某事
sth. cost sb. (money) 某人花钱为了某事
take sb. sometime to do sth. 花某人时间做某事
find out 查明
find sb. doing sth. 发现某人做某事
be angry with sb. 生某人的气
be angry at sth. 生某事的气
the same age as = as old as 与某人年龄一样
he fight with sb. 与某人打架
learn to do sth. 学会做某事
not ... until ... 直到……才……
compare sth.(A) with sth.(B) 把某事(A)与某事(B)作比较
it's time for sth. = it's time to do sth. 到该做某事的时间了
maybe adv. 或许
may be (情态动词 + 动词原形)可能是
shall → should 情态动词 shall 的原形和过去式
pay → paid → paid 动词 pay 的原形、过去式和过去分词
Reading Strategy(阅读方法)
You will learn to use new words better if you use a learner's dictionary. (时刻学着应用新单词来学习比时刻使用字典这种途径方法更好。)A bilingual dictionary sometimes gives the wrong meaning for the situation you want. (在某些你需要的场合下,一本双语字典有时会给你错误的解释。)
Unit 3 What were you doing when the UFO arrived?
重点语法:过去进行时态
do/does 的过去进行时态形式:(was/were) doing
do/does 的过去进行时态的被动语态:(was/were) being done
过去将来时态的肯定句、否定句和疑问句形式:
肯定句例句:I was walking down the street when a UFO landed.
否定句例句:I wasn't walking down the street when a UFO landed.
一般疑问句例句:Were you walking down the street when a UFO landed?
特殊疑问句例句:What were you doing when a UFO landed?
动词 when 和 while 的选择:when 后加瞬间动词,while 后加延续性动词。
例句:The boy was walking down the street when the UFO landed.
=While the boy was walking down the street, the UFO landed.
感叹句
结构:(1) How + adj. + the + 主语 + 谓语动词
=(2) What + (a/an) + [adj.] + n. + 主语 + 谓语动词
例句:What a beautiful flower [it is]!
=How beautiful the flower is!
What beautiful flowers [they are]!
=How beautiful the flowers are!
重点短语:get out 出去;离开
take off 起飞
run away 逃跑;跑掉
come in 进来
hear about = hear of 听说
take place 发生
as ... as 像……一样(eg/ as old as him 像他一样老)
anywhere = everywhere = here and there 任何地方
think about 考虑
think of 认为
get up = get out of the bed 起床
at the doctor's 在诊所
every day 每一天
everyday adj. 日常的
most adj. 大部分
the most 最多的
in space 在太空中
national hero 民族英雄
all over the world = in the world 全世界
Reading Strategy(阅读方法)
The title can be helpful for you to understand a text. (一篇文章的标题可以帮助你理解整篇文章。)It's also a good idea to read the first sentence of each paragraph before you read. (在阅读整篇文章之前,阅读每段的第一句话也是一个很有效的方法。)
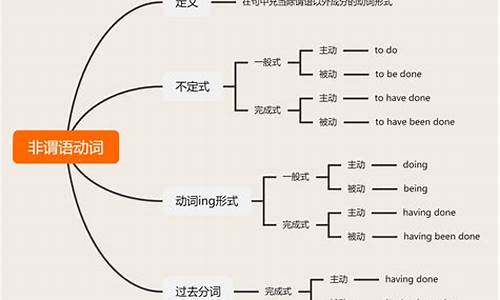
Unit 4 He said I was hard-working.
重点语法:宾语从句
结构:主语 + 谓语动词 + 宾语从句(主语 + 谓语动词 + 宾语/表语)
例句:----I'm good at English. He says. (改为加宾语从句的复合句)
----He says I'm good at English.
注意:①主句是一般现在时态,宾语从句的时态不受其影响。
例句:He says I'm good at English now.
He says I was good at mathematics when I was young.
②主句是过去时态,宾语从句也要用过去时态。
例句:He said I was good at mathematics when I was young yesterday.
He said I was good at English now yesterday.
③宾语从句是客观真理时永远用一般现在时态。
例句:Our teacher says 24 hours make a day.
Our teacher said the sun gives us so many energy yesterday.
④动词原形不能作主语,必须用其 -ing 形式。
例句:She said helping others changed her life.
重点短语:direct speech 直接引语
reported speech = indirect speech 间接引语
first of all = at first 首先
pass on 传递
be supposed to do sth. 应该做某事
be good at = do well in 在某方面做得好
in good health 身体健康
get over 克服
open up 打开
care for = take care of = look after 照料;照顾
not any more = not any longer = no longer 不再
he a cold 感冒
end-of-year exam 年终考试
get nervous 变得紧张
forget to do sth. 忘记做某事(该事未做)
forget doing sth. 忘记做某事(该事已做)
it's + adj. + [for sb.] + to do sth. 做某事[对某人来说]……(加形容词)
context 上下文
Reading Strategy(阅读方法)
First read for meaning, not for detail. (首先理解文段的大致意思,不在于文段的细节部分。)You can understand the meaning of a word you don't know from the context. (至于不懂的单词,你可以通过上下文来寻找它的正确释义。)
Unit 5 If you go to the party, you'll he a great time!
重点语法:if 引导的条件状语从句
结构:主句 + if + 条件状语从句
if + 条件状语从句 + [(comma)] + 主句
注意:在 if 引导的条件状语从句中,主句应用将来时态,状语从句用一般现在时态。
例句:You'll he a great time if you go to the party.
=If you go to the party, you'll he a great time.
重点短语:take away 拿走
around the world = all over the world 在世界各地
make a living 谋生
all the time = always 一直
What's the problem? = What's the matter? = What's wrong? 怎么了?
in order to do sth. 为了做某事
make sb. do sth. 使得某人做某事(to 省略,该结构是一个不带 to 的不定式。)
make sb. adj. 使得某人……(加形容词)
make sb. done 使得某人被做
be famous for 为……而出名
be famous as 作为……而出名
in class 在课堂上
spend ...(time/money) on sth. = spend ...(time/money) in doing sth. 花……(时间/钱)用于做某事
see sb. do sth. 看见某人做某事(强调整个过程)
see sb. doing sth. 看见某人做某事(强调偶然性)
say → said → said 动词 say 的原形、过去式和过去分词
tell → told → told 动词 tell 的原形、过去式和过去分词
eat → ate → eaten 动词 eat 的原形、过去式和过去分词
speak → spoke → spoken 动词 speak 的原形、过去式和过去分词
Unit 6 How long he you been collecting shells?
重点语法:现在完成进行时态
do/does 的现在完成进行时态形式:he/has been doing
do/does 的现在完成进行时态的被动语态:he/has been being done
现在完成进行时态所应用的场合:
①某事从过去发生一直持续到现在都在做
②过去发生的动作对现在造成影响
例:我已上了三年初中。
I he been in Junior School for 3 years.
自从那次他与我谈过心后,我天天都在进步。
I he been making progress since he talked with me that time.
现在完成进行时态的肯定句、否定句和疑问句形式:
肯定句例句:I he been skating for five hours.
否定句例句:I hen't been skating for five hours.
一般疑问句例句:He you been skating for five hours?
特殊疑问句例句:How long he you been skating?
注意:瞬间动词不能和一段时间连用。
例句:你借这本书已经多长时间了?
How long he you been keeping this book?
重点短语:run out of 用完;用尽
by the way 顺便说说
be interested in doing sth. 对某事感兴趣
more than 比……多
far away 在远处
would like to do sth. = want to do sth. = feel like doing sth. 想要做某事
send sb. sth. = send sth. to sb. 把某物赠送给某人
in fact 实际上
room 房间(用于可数名词);空间(用于不可数名词)
common → more common → the most common 形容词 common 的原级、比较级和最高级
Reading Strategy(阅读方法)
Let your eyes "scan" the text quickly to find details that you're looking for. (在阅读文章之前,用眼睛“横扫”整篇文章,快速寻找你需要的文章要点。)You can find information quickly without reading the whole text. (这样你就不用细读整篇文章,就能寻找到你需要的一些信息。)
Unit 7 Would you mind turning down the music?
重点语法:mind [one's] doing sth. 介意(某人)做某事
重点短语:not at all 一点也不
turn down 调节使音量变小
right away = in a minute = at once 立刻;马上
wait in line 排队等候
cut in line 插队等候
hasn't = has not
keep ... down 压低声音;使缓和
at first = first of all 首先
take care 当心;小心
take care of = care about = look after 关心;照顾
break the rule 违规
obey the rule 遵守规定
put out 熄灭
pick sth. up 捡起某物
wait for sb. 等候某人
depend on 依赖;依靠
get back = return 要回
mean → meant → meant 动词 mean 的原形、过去式和过去分词
Reading Strategy(阅读方法)
As we read, we need to find "topic sentences".(在我们阅读的时候,我们需要寻找“主题语句”,也就是和文章中心最相关的语句。) These sentences usually gives us a "summary", or overall meaning of each paragraph and help us understand what the paragraph is about.(这些语句通常会给我们一些文章的“概要”,或者每个文段的全部意思,来帮助我们理解段落大意。) After the topic sentence comes more detail and explanation.(当“主题语句”出现后,该段的一些解释和细节也就会随之出现。)
Unit 8 Why don't you get her a scarf?
重点语法:询问别人为什么要做或者不做某事
why don't you do sth. = why not do sth.
例句:Why don't you get her a camera? = Why not get her a camera?
what about = how about
例句:How about some tennis balls? = What about some tennis balls?
重点短语:fall asleep 入睡
give away 赠送;分发
hear of = hear about 听说
take an interest in = be interested in 对……感兴趣
make friends with 与……交友
make progress 取得进步
keep → kept → kept 动词 keep 的原形、过去式和过去分词
feed → fed → fed 动词 feed 的原形、过去式和过去分词
fall → fell → fallen 动词 fall 的原形、过去式和过去分词
hear → heard → heard 动词 hear 的原形、过去式和过去分词
Reading Strategy(阅读方法)
To understand the important ideas from the text, we must "summarize".(为了了解文段最主要的意图,我们必须要进行总结。) Do this by answering "who, what, where, why" questions as you read.(在阅读时,常注意回答时间、地点、人物这些基本要素问题,达到总结的目的。)
Unit 9 He you ever been to an amusement?
重点语法:现在完成时态
do/does 的现在完成时态形式:(he/has) done
do/does 的现在完成时态的被动语态:(he/has) been done
现在完成时态主要强调过去发生的事情对现在的影响。
例句:我去年去过美国,那是我第一次出国。
I he ever been to America. It's the first time for me to go abroad.
重点短语:he a great time = he a good time = he fun = enjoy oneself 玩得高兴
on board 在船上
end up doing sth. 结束做某事
all year round = all over the year 终年
understand → understood → understood 动词 understand 的原形、过去式和过去分词
Reading Strategy(阅读方法)
After reading, write down three or more things you he learned. (在阅读整篇文章之后,把你学到的三样或更多事物写下来。)We always remember things better if we take time to reflect. (如果我们花时间去思考一些问题的话,那么我们就能更容易地记住一些事情。)
Unit 10 It's a nice day, isn't it?
重点语法:反意疑问句
反意疑问句由肯定陈述句加否定问句构成,或者由否定陈述句加肯定问句构成。
例句:He's a student, isn't he?
She's not his mother, is she?
回答反意疑问句时,要根据事实来回答。若事实是肯定的,则必须用 yes 回答。若事实是否定的,则必须用 no 回答。
例句:你还没有准备好,对吧?
You're not ready, are you?
是的,我没有准备好。
No, I'm not.
不,我准备好了。
Yes, I am.
重点短语:look through 浏览
come along 出现;发生
get along 相处
at least 至少
at most 至多
a thank-you note 感谢信
forget → forgot → forgotten 动词 forget 的原形、过去式和过去分词
little → less → least 形容词 little 的原级、比较级和最高级
many/much → more → most 形容词 many/much 的原级、比较级和最高级
小升初英语语法强调句知识点总结
要想学好英语,就必须学好英语知识点,那么初中英语宾语从句知识点有哪些呢?以下是我分享给大家的初中英语宾语从句知识点,希望可以帮到你!
初中英语宾语从句知识点
一、.引导词
1.从句为陈述句,常选择引导词that,that引导宾语从句无意义,不充当句子成分常省略。例句:He told us (that) they would help us through the whole work.
2.从句为一般疑问句,常选择引导词if或whether,表示?是否?。在 whether ? or not 结构中不能用 if 替换。例句:I don?t know if there will be a bus any more.
3. 从句为特殊疑问句,常选择what,when,where,which,who,how等的疑问代词、副词作引导词。 例句:He didn?t tell me when we should meet again.
二、判断时态情况:
1.主句是一般现在时,从句可以为各种时态。
2.主句是一般过去时,从句要用相应过去时态。
注意:从句描绘客观事实、真理、自然现象等,从句时态不受主句时态限制,仍用一般现在时。
例句:He answered that he was listening to me.
Father told me that practice makes perfect .
三、宾语从句的语序要用陈述句语序
陈述句语序,就是主语在前,谓语动词在后。
错误: He is wondering when can he finish this difficult job.
正确: He is wondering when he can finish this difficult job.
注意:宾语从句的否定转移
主句的谓语动词是think,believe,imagine,suppose,consider,expect,fancy,guess等,并且主句的主语是第一人称而且为一般现在时,从句的否定词一般要转移到主句上来,其反义疑问句一般与宾语从句一致.例如; I don?t think he will come to my party.而不能说成I think he won?t come to my party.
初中英语宾语从句知识点常见考法
对于宾语从句的考查,多以单选的形式考查学生灵活运用的能力。一般情况下,常从引导词的选择、时态的一致性及从句的陈述语序方面考查。
典型例题:Please tell me ______ last year.
A.where does your sister work B where did your sister work
C .where your sister works D where your sister worked
解析:本题考查对宾语从句的掌握。宾语从句要用陈述语序,所以排除A和 B;last year 表示过去时 ,所以排除 C 。
答案:D
误区提醒
宾语从句的语序要用陈述句语序 ,但要注意当疑问词为主语时,句式为:疑问词+谓语+其他 ,问句和陈述句语序一样。
典型例题:I didn't know ?
A. What wrong was with her B.what was wrong with her
C .what wrong is with her D.what is wrong with her
解析:主句是一般过去时,从句要用相应过去时态,所以排除C和D;在what was wrong with her中,what作主语,所以问句本身又是陈述句语序,不用变化。
答案: B
学好初中英语的建议
积累词汇
如果你是学生,可以通过英语课程,让老师帮助你了解英语的基础知识和思维方式。如果你是自学者,可以通过网络,根据上的内容了解英语的基础知识等。并且需要购买一本中英的英语词典,让你在学习英语的前期掌握足够的英语词汇。
学习语法
语法是语言的?骨架?,是词形变化规则和组词成句规则的总和,也是研究词的结构、用词规则、组合词语、句子结构等一系列规律的专门科学。具有概括性、生成性、稳定性 和系统性的特点。学习语法的目的,是为了可以更好地进行听说读写等语言实践活动。也就是说,通过对语法规则规律的掌握,减少在语言实践练习中的盲目性,提高语言的准确性。学习语法可以通过课本、书籍、网络等方法加强练习。
多读、多背、多写
学好英语,还要有坚持不懈的精神,不经历背诵大量文章,写大量东西,听大量文章(读报、听广播、看外语**、听外语讲座、读书籍)是根本不可能达到目的的,因为学习语言需要对我们的各种感观进行刺激,每天至少看 60-120分钟的英语,早晨和晚上是学英语的最好时间。
勇于交流
前面3点可以让你很好的读和写了,但是只会读和写对于学习一门语言来说是远远不够的,我们还要学会怎样与人交流。敢于开口说英语,不要怕犯错误,都会犯错,这是在所难免的,加强交际训练,为自己提供一个英语环境,只有多交流,才能把口语说的很流利。
猜你喜欢:
1. 初中英语重点知识点的总结
2. 初三英语重点知识点的归纳
3. 初中必备的英语知识点总结
4. 初二英语重点语法知识点归纳
5. 初三英语必备的语法知识点
关于英语感叹句的知识点 来几个典型句子并总结,谢谢
小升初英语语法强调句知识点总结
英语语法是针对英语语言进行研究后,系统地总结归纳出来的一系列语言规则。英语语法的精髓在于掌握语言的使用。下面我整理的小升初英语语法强调句知识点总结,一起来看看吧。
小升初英语语法强调句知识点总结1
前面讲到强调时间状语时,通常要用it is…that…,而不用it is … when…,所以有的同学对于下题选择了A:
It was ten o’clock ______ he came back.
A. that B. when
C. so D. which
其实此题最佳答案为B,这不是一个强调句型。When引导的是一个时间状语从句,全句意为:当他回来时,时间是10点钟。比较以下强调句型:
It was at ten o’clock that he came back. 他是10点钟回来的。
It was after ten o’clock that he came back. 他是在10点过后回来的。
It was before ten o’clock that he came back. 他是在10点前回来的。
再比较:
It is autumn when lees fall. 当树叶落的时候就是秋天了。
It is in autumn that lees fall. 树在秋天落叶。
另外,下面的句子也不是强调句型:
1) It’s a long time ______ I met you last.
A. that B. since
C. when D. which
2) It was more than a year now _____ he had seen her.
A. that B. since
C. when D. which
3) Was it here _____ you were away talking to a friend? Sure. But when I got back there, it was gone.
A. that B. while
C. which D. where
以上三题均选B,即前面两句填since,其意为自从;第(3)填while,其意为 在…期间。
2. 将强调句判为非强调句
有些强调句型由于句子本身有一定的特殊性,比如是强调句的特殊疑问句形式,强调句型情态动 词或复杂时态等,强调句中的被强调成分过于复杂,强调句与其他从句混杂在一起,等等,这都可能掩盖 强调句型的本来面目,从而导致误判:
1) When was _____ that the general manager left for Japan?
A. he B. it
C. that D. since
答案选B,为强调句的特殊疑问句形式。
2) It might he been John _____ bought a present for Mary yesterday.
A. that B. when
C. what D. which
答案选A,为强调句型,只是其中的动词be用了might he been这一复杂结构。
3) It was what he meant rather than what he said ______ annoyed me.
A. which B. as
C. what D. that
答案选D,为强调句型,被强调部分为 what he meant rather than what he said,句意为 让我生气的不是他说的话,而是他话中的意思。
4) It was just in the room _____ he was born _____ he died.
A. where, which B. that, that
C. where, that D. which, that
答案选C,为强调句型,被强调成分是 in this room,where he was born 为修饰 the room 的 定语从句。
5) It was lack of money, not of effort, _____ defeated their plan.
A. which B. as
C. that D. what
答案选C,为强调句型,被强调成分为 lack of money, not of effort。
小升初英语语法强调句知识点总结2一、考查结构词的`选择与使用
强调句的基本结构是It+be+被强调成分+that (who)…,其中的结构词it 和that (who)为高考英语考查强调句时最常考查的考点。如:
1. I don’t mind her criticizing me, but _________ is how she does it that I object to.
A. it B. that C. this D. which
解析答案选A。此题考查it is ...that…这一强调句句型。句意为:我不介意她批评 我,我反对的是她批评我的方式。句中空格处填强调句结构词it。
2. It is not who is right but what is right _________ is of importance.
A. which B. it C. that D. this
解析答案选C。此题考查it is…that…这一强调句式,被强调的是not who is right but what is right,全句意为:重要的不是谁是对的,而是什么才是对的。句中空格处填强调句 结构词that。
二、考查强调句的特殊疑问句形式
强调句型的陈述句形式和一般疑问句形式一般还好理解,但若以特殊疑问句形式出现,则很容易 误解。比较:
Jim told us the news.(非强调句)
It was Jim that told us the news.(强调句型的陈述句形式)
Was it Jim that told us the news?(强调句型的一般疑问句形式)
Who was it that told us the news?(强调句型的特殊疑问句形式)
特殊疑问句形式的强调句可视为对陈述句强调中的被强调成分提问得来,如对It was yesterday that he arrived. 这一句中的yesterday提问,即得到When was it that he arrived?
请看高考真题:
1. I just wonder _________ that makes him so excited.
A. why it does B. what he does C. how it is D. what it is
解析答案选D。注意what it is that makes him so excited为宾语从句,用作动词wonder 的宾语。如果去掉主句I just wonder将原句改为疑问句则是:What is it that makes him so excited?
2.— _________ that he manage to get the information?
—Oh, a friend of his helped him.
A. Where was it B. What was it C. How was it D. Why was it
解析答案选C 。由答语的内容可知,空格处应填how。
三、考查not…until…句式的强调句形式
not...until用于强调句型时的基本形式为It is (was) not until…that…。如:
1. It _________ we had stayed together for a couple of weeks _________ I found we had a lot in common.
A. was until; when B. was until; that
C. wasn’t until; when D. wasn’t until; that
解析答案选D。此题考查not…until…句式的强调形式。又如:It was not until she took off her dark glasses that I realized she was a famous film star. 直到她取下墨 镜,我才意识到她是一位著名影星。
2. It was not until she got home _________ Jennifer realized she had lost her keys.
A. when B. that C. where D. before
解析答案选B。考查not…until…句式的强调形式。又如:It was not until I met you that I knew real hiness. 直到我遇到你以后,我才真正体会到幸福。
四、考查强调句与非强调句的辨别
1. It will soon be five years _________ we came to live in Cairo.
A. that B. when C. since D. as
解析答案选C。此题不是考查强调句型,而是考查since的用法,句意为我们来到开 罗居住快五年了。又如:It is two years since he left the country. 他离开这个国家已经两 年了。/ It’s quite some time since we wrote to each other. 我们互相通信已有不少时间了 。
2. Was it here _________ you were away talking to a friend? Sure. But when I got back there, it was gone.
A. that B. while C. which D. where
解析答案选B。此题不是考查强调句型,而是考查while的用法,while在此表示在 ……期间,句意为:当你离开去跟朋友说话的时候它在这儿吗?
小升初英语语法强调句知识点总结31.Were all three people in the car injured in the accident?
No,___ only the two passengers who got hurt.
A. it was B. there is
C. it were D. there was
2. ---Who is making so much noise in the garden? --- ___ the children.
A. It is B. They are
C. That is D . There are
3. It was ___she was about to go out ___the telephone rang.
A. when that B. so; that
C. before; then D. when; before
4.It was ___ he said ___ disointed me.
A. what; that B. that; what
C. that; when D. it; when
5.____ that silver is not widely used as a conductor?
A. Why is B. Is it why
C. Why is it D. Why is that
6.I can’t find Mr. Smith .Where did you meet him this morning? It was in the hotel ___ he stayed.
A. that B which
C. the one D. where
7.It was in the small house ___was built with stones
by his father ___ he spent his childhood.
A. which; that B. that where
C, which; which D. that; which
8.It was ___ it was raining so hard that we had to stay at home all day.
A. since B .for
C. as D. because
9.Is ____three hours ____ the boy ___family is poor to come to school on foot?
A .it that; whose B. it; that it takes; whose
C. it for that it takes; whose D. it; when that
10.It was his wife___ left him without saying goodbye.
A. who B .which
C .when D. in which
11. It is on a winter night ___he spent with me last night.
A. that B. where
C. as D .when
12 It is the young man ___ looked for ___ caught the murderer.
A.that; who B.that; they
C. they that D they which
13.It was ____ my teacher worked ____ I work hard.
A. where; that B. where; where
C .that; that D. that where
14.It was in the evening__we reached the little town of Winchester.
A that B. until
C. since D. before
15.It was not until dark ___ he found ___ he thought was the correct way to solve the problem.
A. that; what B. that; that
C. when; what D. when; that
16.It is the ability to do the job ____ matters ,not where you come from or what you are.
A. one B. that C .what D. it
17. I don’t know ____ that you stay here.
A. how long it is B. how long is it
C. it is how long D. is it how long
18.It was _____ that caused him to serve dinner an hour later than usual.
A. we being late B. our being late
C. we were too late D. because we were late
19.---what was the party like?
---Wonderful. It’s years _____ I enjoyed myself much.
A. after B. before C .that D. since
20.Why! I he nothing to confess(承认). ____you want me to say.
A.What is it that B.What it is that
C.How is it that D. How it is that
答案
1~10 AAAAC DADBA
11~20 ACAAA BABDB
小升初英语语法强调句知识点总结4强调句型是英语语法考试经常涉及的一个考点,这类考题主要涉及以下几个方面:
一是考查强调句型的基本结构,即It is + 被强调成分 + that / who +其他部分 ;
二是考查强调句的疑问句形式,如强调句的一般疑问句形式Is it + 被强调成分 + that / who +其他部分以及特殊疑问句形式疑问词+is it that+其他部分;
三是考查not…until…的强调形式It was not until….that….。如:
It was from Betty that he first heard the news. 这消息他最早是从贝蒂那里听到的。
Was it you who broke the window? 窗子是你打破的吗?
It was not until the rain stopped that they started. 直到雨停他们才出发。
How long ago is it that you last saw her? 你上次看见她是多久以前的事?
请看有关几道考题(答案在题后)
1. It wasn’t until nearly a month later _________ I received the manager’s reply.
A. since B. when C. as D. that
2. It is what you do rather than what you say _________matters.
A. that B. what C. which D. this
3.— _________ that he manage to get the information.
—Oh, a friend of his helped him.
A. Where was it B. What was it C. How was it D. Why was it
4. It was _________back home after the experiments.
A. not until midnight did he go B. until midnight that he didn’t go
C. not until midnight that he went D. until midnight when he didn’t go
5. It is these poisonous products _________ can cause the symptoms of the flu, such as headache and aching muscles.
A. who B. that C. how D. what
6. It was for this reason _________ her uncle moved out of New York and settled down in a small village.
A. which B. why C. that D. how
7. It is the ability to do the work _________ matters not where you come from or what you are.
A. one B. that C. what D. it
答案:DACCBCB
;谁能帮忙总结一下有关于倒装句的知识,具体如下
感叹句的结构:
What + 名词词组 + 主谓部分(在不影响句意的情况下,主谓部分可以省略)
例:1.What a long way(名词词组) it is from Beijing to London!
北京离伦敦是多么远啊!
2.What good news!(由于news是不可数名词,所以不加a)
多么好的新闻啊!
3.What noise(名词) they are making!
他们是多么吵啊!
4.What a wonderful evening(名词词组) we he had!
我们拥有多么美好的夜晚啊!
How + 形容词/副词 + 主谓部分
例:1.How beautiful(形容词) the present is!
这份礼物是多么漂亮啊!
2.How well(副词) the boy speaks English!
这个男孩的英文说得多好啊!
3.How hard(副词) all these people are working!
这些人工作得多么辛苦啊!
4.How bright(形容词) a girl she is!
这个女孩是多么聪明啊!
How + 一个陈述句子
例:1.How I wish I could walk on the moon!
我是多么希望到月亮上走走!
2.How I wish to pay a visit to London!
我是多么希望去伦敦旅游啊!
3.How we enjoyed ourselves!
我们是多么快乐啊!
How + 主语 + 谓语How还可以修饰动词,对动词进行感叹,也是对整个句子的感叹
例:1.How he runs!
他跑(得多快)啊!
2.How things are changing!
事物变(得多快)啊!
一般地说,
How + 形容词/副词 + 主语 + 谓语
What a/an + 形容词 + 名词 + 主语 + 谓语注意,如果此时的名词是不可数名词,不应加a或者an
高一英语语法知识点归纳总结
描述:
主语和谓语是句子的核心,它们之间有两种语序:一是主语在谓语之前称为自然语序(Natural Order);二是主语在谓语之后则称为倒装语序(Inverted Order)。而倒装语序中又有全部倒装(Full Inversion)和部分倒装(Partial Inversion)两种情况。
首先,在全部倒装的句子中,要把整个谓语放在主语的前面去而构成倒装语序。
例如:
There are large numbers of students in the lecture hall.
(在There be…的句式中,There只是个引导词而不是主语,真正的主语是后面作表语的名词或者名词短语。因此,There be…的句式都是全部倒装的句子。)演讲厅里有大量的学生。
When he ran to the door, there stood a mid-aged man with a lantern in his hand .
(此句是为了"描述情节的需要",把倒装当着修辞的手段而写成了全部倒装句。句子的主语是a mid-aged man,谓语是stood 。)当他向房门跑去时,那儿正立着一位手里拿着一盏灯笼的中年男人。
另外,在部分倒装的句子中,只把谓语的一部分(如情态动词、助动词、或是系动词be)放到主语的前面去,构成倒装语序。例如:
Are you going to take part in the football match against Accounting Department on Friday afternoon? (句子的谓语是are going to take part,are是句子的谓语的一部分;句子的主语是you 。所以,此句是部分倒装的句子。疑问句都是部分倒装句。)你打算去参加星期五与会计系进行的足球赛吗?
Hardly could he finish his test paper when the school bell rang .(由于语法要求的原因,本句写成了部分倒装的句子。它的自然语序应该是:When the bell rang, he could hardly finish his test paper.)他还未做完试卷,下课铃就响了。
了解了倒装语序的构成情况后,我们再来看看倒装语序在各种不同类句子中的使用情况:
A. 在疑问句中
各种疑问句一般地说都是倒装语序。例如:
Will they come to see us this weekend ? 这个周末他们将来看我们吗?
Are you talking about the film you saw last Monday ?
你们是在谈论你们上周一看的那部**吗?
Can you speak another foreign language except English?
除开英语,你还能说另一种外语吗?
Where did you buy the dictionary, in the book store nearby or in Xinhua bookstore?
你在哪儿买的这本词典,是在附近的书店还是在新华书店?
She is not a student, isn't she ? 她不是个学生,对吗?
B. 在感叹句中
某些感叹句也用倒装语序。例如:
Isn't it a beautiful garden ! 多么美丽的花园啊!
What a beautiful garden it is ! 多么美丽的花园啊!(在这种句式中,主语在谓语之前,属于自然语序。对于主语和谓语而言,语序没有倒装。)
He you ever seen such a naughty kid like him !
你见过那个孩子像他这么调皮!
C. 在陈述句中
陈述句在一般情况下用自然语序;但由于英语语法的某些原因,陈述句也要使用倒装语序。这些原因大致可以归纳如下:
1) 为了避免句子部分内容不必要的重复,常用"so + be动词(助动词、情态动词)+主语"或"neither / nor + be动词(助动词、情态动词)+主语"的倒装句式。其中第一个句式表示"与前面所述的肯定情况相同", 第二个句式表示"与前面所述的否定情况相同"。例如:
His brother is a college student; so is mine.
他弟弟是大学生,我弟弟也是。
His brother is not a college student; nor is mine .
他弟弟不是大学生,我弟弟也不是。
He used to he his further study abroad; so did I.
他曾去国外深造过,我也去过。
He didn't use to he his further study abroad; neither did I.
他没去国外深造过,我也没有。
One of my friends can speak three foreign languages; so can his wife.
我的一个朋友会说三门外国语,他的妻子也会。
One of my friends cannot speak three foreign languages; neither can his wife .我的一个朋友不会说三门外国语,他的妻子也不会。
They are now preparing for their final examinations; so are we .
他们正在为期末考试作准备,我们也一样。
They are not now preparing for their final examinations; nor are we .
他们没在为期末考试作准备,我们也没有。
2)具有否定意义的词或短语置于句首时(除否定词修饰主语外),句子一般要写成部分倒装句。这类词或短语常见的有:not, never, seldom, hardly, rarely, scarcely, by no means, under no circumstances, in no way, at no time, no sooner … (than), hardly … (when), not only … (but also), not until… ,等。例如:
Hardly had she sat down when she heard someone knocking at the door .
她还没来得及坐下来,就听见有人敲门。
Not until twelve o'clock did he go to bed last night .
他昨晚直到十二点钟才睡觉。
Never he my sisters been to Hong Kong before .
我的妹妹们以前从未去过香港。
No sooner had I returned home from New Zealand than I bought a house and went to live there.我从新西兰一回国,就买了一栋房子并在那儿住下了。
So far as I know, seldom does Mary come back to see her mother.
就我所知,玛利几乎很难回来看她妈妈。
Scarcely a drop of rain fell here last fall . (否定词修饰主语时,句子不用倒装。) 去年秋天,这儿几乎没下一滴雨。
3)当so, often, only等表示程度、频率的副词放在句首时,句子一般要倒装。例如:
Only in this way can you come up with a solution to the problem.
只有这样,你才有可能想出解决这个问题的办法。
So serious was the situation that everybody faced a test.
形势如此地严峻,每个人都面临着一场考验。
So hard did he overwork that he fell ill at last. 他太操劳过度以致最后病倒了。
4)当there, here, then, now等副词在句首,且谓语是come, go, be等动词时,句子一般要全部倒装。其意义在于引起他人的注意。如果这类句子的主语是代词,则不用写成倒装句。例如:
Now, here goes the story.这个故事是这样的。
Look, there comes the taxi.瞧,出租车过来了。
Then came another question.然后又一个问题提出来了。
Then followed the four-year War of Liberation.接下来是四年的。
5) 当out, in, away, up, bang等表示方位或拟声词放在句首时,句子一般要全部倒装。这类子比自然语序的句子更为生动、形象。但如果这类句子的主语是代词,则不用写成倒装句。例如:
Bang goes my ace.我砰地一下打出了"A"。(牌中的点数)
Away flew the bird.那鸟飞走了。
Suddenly, in came a man with a mask on his face.
突然进来一个蒙着面具的人。
6) 其他情况还有:省略了if的虚拟条件句、某些表示祝愿的句子、以及某些让步状语从句,等等也要用倒装句式。例如:(省略了if的虚拟条件句)
Had they not helped us, we could not he done it so successfully.
如果没有他们的帮助,我们不可能把那件事办的如此成功。
Should he come, say "Nobody in" to him.
万一他来了,对他说:"公司没人。"(某些表示祝愿的句子)
May our friendship last forever.愿我们的友谊常存!
May your company become prosperous.祝贵公司生意兴隆!(某些让步状语从句)
Try as I might, I couldn't lift the stone.无论我使多大的劲,我也无法搬起那块石头。
They said they would follow the Party's lead come what might.
他们说无论发生什么情况,他们都会跟党走的。
7) 由于修辞或是平衡句子的原因也可以用倒装句;也可以不用。这不是一条必须的规定。
Next to this one is another grand hotel which is beautifully decorated .
这家饭店隔壁还有一家装修华丽的大饭店。
On either side of the great enue stood many block buildings.
这条大街的两侧都耸立着许多综合楼。(这类句子也可以不用倒装句。)
"I'm leing for Beijing tomorrow," said Tom to his mother (OR: Tom said to his mother) .汤姆对他妈妈说:"我明天动身去北京。"
Many block buildings stood on either side of the great enue.
许多综合楼耸立在这条大街的两侧。
Another grand hotel, which is beautifully decorated, is next to this one .
这家饭店隔壁还有一家大饭店,那家饭店装修十分华丽。
“倒装句”在汉英词典中的解释(来源:百度词典):
1.[Grammar] an inverted sentence; a sentence in inverted order
倒装句之全部倒装
全部倒装是只将句子中的谓语动词全部置于主语之前。此结构通常只用与一般现在时和 一般过去时。常见的结构有:
1) here, there, now, then, thus等副词置于句首, 谓语动词常用be, come, go, lie, run。
There goes the bell.
Then came the chairman.
Here is your letter.
2) 表示运动方向的副词或地点状语置于句首,谓语表示运动的动词。
Out rushed a missile from under the bomber.
Ahead sat an old woman.
注意:上述全部倒装的句型结构的主语必须是名词,如果主语是人称代词则不能完全倒装。
Here he comes. Away they went.
倒装句
一.概念:
英语句子通常有两种语序:一种主语在前,谓语在后,称为自然语序,另一种谓误在前,主语在后,称为倒装语序
二.相关知识点精讲
按“主语+ 谓语” 这种顺序排列的句子是陈述语序。如果排列顺序变为“谓语( 或谓语一部分)+主语”,就是倒装。倒装句分为:
完全倒装: 整个谓语移至主语前面叫完全倒装 。
部分倒装: 只把助动词、系动词或情态动词放在主语之前叫部分倒装 。
三、作用
通常是希望强调句中的某一部分
1. 当以there, here, out , in , up , down, away 等副词开头的句子,为了起到强调的作用,可构成倒装句,只把副词放在句首,主语和谓语位置调换,不加助动词。
Our teacher came in.
In came our teacher.
这种倒装要求:主语必须是名词。主语是人称代词时,主语和谓语语序不变。
Here it is.
Away he went.
这类倒装句式一般只用一般现在时和一般过去时。
Here comes the bus.
Out rushed the boys.
2. how, then, just, often 表示时间的副词放在句首,可构成倒装句,只把副词放在句首,主语和谓语位置调换,不加助动词。
Then came 8 years of the Anti Japanese War.
3. 表地点状语的介词短语放在句首,要用倒装句式,以示强调。
这种倒装句也是主谓直接调换位置,不加助动词did, does或do.
Under a big tree ________, half asleep.
A. did sat a fat man B. a fat man sat
C. did a fat man sat D. sat a fat man
4. there放在句首时,要用倒装句式。
在“there + be”结构中的谓语动词有时不用be , 而用表示类似“存在”观念的其他不及物动词。如:live, stand, come, lie, flow, enter, rise 和ear等。
There came shouts for help from the river.
There lies a large wheat field in front of the house.
Many years ago there lived an old man in the wooden house.
In front of the tower flews a stream.
5. so + 动词+主语
neither/ nor + 动词+主语
表示两人的同样一个情况时,只能表示一件事,即上、下句所使用的动词、时态要一致。
否则要用so it is with…
You can ride a bike. So can I .
He has been to Beijing. So he I .
The first one isn’t good, neither is the second.
His uncle is a worker and has been working in the factory for more than ten years. So it is with his aunt.
6. so+ 形容词/副词that 的结构状语从句可以用正常语序表示,也可以把so+形容词/副词放于句首构成倒装。句型如下: so +形容词/副词+be/助动词/情态动词that +从句。
Light trels so fast that it is difficult for us to imagine its speed.
= So fast does light trel that it is difficult for us to imagine its speed.
So easy was the work that they finished it in a few days.
7. done做形容词在句中做表语时,常把表语放在句首,要用倒装句式。
Gone forever are the days when the Chinese people had to use foreign oil.
8. 否定副词not , never, seldom, nowhere, little , rarely 放于句首时要用倒装句式。
We seldom get up at four in the morning.
= Seldom do we get up at four in the morning.
Not a single word from him could the enemy drag.
Rarely he I heard of such a silly thing.
9. hardly…when; scarcely…when…; no sooner…than… 可以用正常语序 had hardly done when… did 或用倒装句式Hardly had + 主语+ done when… did 句式。hardly所在的句子用过去完成时。
The bell hardly had rung when the class began.= Hardly had the bell rung when the class began.
No sooner had he arrived in Beijing than he began to work.
10. not only… but also 如连接两个成分时,不用倒装;连接句子时, 前面的句子要用倒装。
Not only was everything that he had taken away from him, but also his German citizenship.
Not only is he busy, but also I he a lot of work to do.
Not only does he speak English very well, but also he speaks French well.
11. only 及所修饰的副词、介词短语或状语从句放在句首时,要用:
only+ 状语+ be /助动词/情态动词+主语及其他
Only when he told me the news did I know what had hened.
Only in this way can you make progress in your English.
12. 虚拟语气中的倒装句
If I were you, I would take the job. = Were I you, I would take the job.
三.巩固练习
1._______ and caught the mouse.
A. Up the cat jumped B. The cat up jumped
C. Up jumped the cat D. Jumped up the cat
2.______ and the lesson began.
A. In came Mr Brown B. Mr Brown in came
C. In came he D. came in Mr Brown
3.Over _______ , dead.
A. rolling the goat B. rolled the goat
C. did the goat roll D. the goat rolled
4.—Where is my shirt, mum? —_________.
A. There is it B. There it is
C. There is D. Here is it
5. —Where is your father? —Oh, ________.
A. here he comes B. he here comes
C. here does he come D. here comes he
6.The door opened and there ________ .
A. enters an old man
B. entered an old man
C. did an old man enter
D. an old man entered
7. Now ______ your turn to recite the text.
A. will come B. comes C. has come D. there is
8.Often _____ them not to smoke here.
A. we advised B. advised me
C. did we advise D. had we advised
9.________ playing soldiers.
A. Inside the room were two boys
B. Inside the room two boys
C. Were two boys inside the room
D. Inside the room was two boys
10. On the wall _______ two large portraits.
A. are hanging B. hanged C. hang D. hangs
11._______ who was wounded in the stomach.
A. Among them were a soldier B. Among them was a soldier
C. Among them a soldier was D. Among they was a soldier
12. Next door to ours ________ , who is no less than eighty.
A. that lives an old man B. does an old man live
C. lives an old man D. where lives an old man
13.She plays the piano very well, ______.
A. so every one of us does B. every one of us does
C. so does every one of us D. so do every one of us
14.You say he works hard, ______, and _____.
A. so he does; so you do B. so he does; so do you
C. so does he; so do you D. so does he; so you do
15. —I thought you women were present at the meeting. —__________.
A. So we were B. So we did C. So were we D. So did we
16.I don’t think Jack will come today, _____.
A. nor will Mary B. and Mary doesn’t
C. Mary will either D. or Mary does
17. She is fond of cooking, _____I .
A. so am B. nor am C. neither do D. nor do
18.Marx was born in Germany and German was his native language .
A. So it was with Engles B. So was it with Engles
C. So was Engles D. So did Engles
19.A fish needs water and without water it will die._______.
A. So does a man B. So will a man
C. So it is with a man D. So is it with a man
20. So absorbed _______ the work that she often forgot to _____ her meals.
A. had she been in; do B. she was in; make
C. was she in; take D. she had been in ; he
21.So loudly ______ that every one of the class could hear him.
A. did he speak B. did he spoke C. spoke he D. he spoke
22. __________ his erance that no one could recognize him.
A. Strange so was B. So strange was
C. Was so strange D. So was strange
23.Not once ______ their plan.
A. did they change B. they changed
C. changed they D. they did change
24. Never ______ such a wonderful place as Hangzhou.
A. are seeing B. had I seen
C. I he seen D. he I seen
25.Seldom ______ TV during the day.
A. they watch B. are they watching
C. he they watched D. do they watch
26.Nowhere ______ as in my garden.
A. the flowers were so beautiful
B. were the flowers so beautiful
C. so beautiful were the flowers
D. so beautiful the flowers were
27. Hardly ________ his homework when he went out.
A. finished he B. he had finished
C. did he finish D. had he finished
28.Scarcely _____ finished their homework ______ I came into the classroom.
A. had they; than B. they had; when
C. had they; when D. did they; when
29. Not only _______ a promise, but also he kept it.
A. has he made B. does he make
C. he made D. did he make
30. Not until his comrades criticized him _______ to admit his mistake.
A. had he begun B. began he
C. did he begin D. does he begin
四.答案
1—5 CABBA 6—10 BBBDA
11—15 BCCBA 16—20 BAACC
21—25 ABADD 26—30 BDCDC
高中英语语法知识点总结
高一是踏入高中的第一个阶段,所以我们要努力打好英语的基础。那么高一英语语法知识点的归纳总结有哪些呢?下面是由我为大家整理的“高一英语语法知识点归纳总结”,仅供参考,欢迎大家阅读。
高一英语语法知识点归纳总结高一英语语法
表语从句
表语从句在复合句中作表语的名词性从句,放在系动词之后,一般结构是“主语+连系动词+表语从句”。可以接表语从句的连系动词有be, look, remain, seem等。引导表语从句的that常可省略。另外,常用的还有the reason is that… 和It is because 等结构。例如:
1) The question is whether we can make good preparation in such a short time.
2) This is why we can't get the support of the people.
3) But the fact remains that we are behind the other classes.
4) The reason he is late for school is that he missed the early bus.
高一英语语法2
过去进行时
1. 表示过去某时正在进行的动作。
[例句] He was sleeping when Mary came to see him.
2. 动词go, come, lee, arrive, start等的过去进行时常表过去将来时。
[例句] She said she was going to Beijing the day after tomorrow.
高一英语语法3
宾语从句
宾语从句就是在复合句中作宾语的名词性从句,通常放在主句谓语动词(及物动词)或介词之后。
1.作动词的宾语
(1)由that引导的宾语从句(that通常可以省略),例如:
Iheardthatbejoinedthearmy.我听说他参军了。
(2)由what,whether(if)引导的宾语从句,例如:
a)Shedidnotknowwhathadhened. 她不知道发生了什么。
b)Iwonderwhetheryoucanchangethisnoteforme. 我想知道你是否能帮我改一下笔记。
(3)动词+间接宾语+宾语从句。例如:
Shetoldmethatshewouldacceptmyinvitation. 她对我说她会接受我的邀请。
2.作介词的宾语,例如:
Oursuccessdependsuponhowwellwecancooperatewithoneanother. 我们的成功取决于我们之间的合作。
3.作形容词的宾语,例如:
Iamafraid(that)I’vemadeamistake. 我恐怕我已经犯了一个错误。
注意:that引导的从句常跟在下列形容词后作宾语:anxious,aware,certain,confident,convinced,determined,glad,proud,surprised,worried,sorry,thankful,ashamed,disointed,annoyed,pleased,hurt,satisfied,content等。也可以将此类词后的that从句的看作原因状语从句。
4.it可以作为形式宾语
it不仅可以作为形式主语,还可以作为形式宾语而真正的宾语that从句则放在句尾,特别是在带复合宾语的句子中。例如:
Wehearditthatshewouldgetmarriednextmonth.我听说她下个朋就会结婚了。
5.后边不能直接跟that从句的动词
这类动词有allow,refuse,let,like,cause,force,admire,condemn,celebrate,dislike,love,help,take,forgive等。这类词后可以用不定式或动名词作宾语,但不可以用that引导的宾语从句。如:
正确表达:Iadmiretheirwinningthematch.
错误表达:Iadmirethattheywonthematch.
6.不可用that从句作直接宾语的动词
有些动词不可用于“动词+间接宾语+that从句“结构中,常见的有envy,order,accuse,refuse,impress,forgive,blame,denounce,advise,congratulate等。例如:
正确表达:Heimpressedthemanagerasanhonestman.
错误表达:Heimpressedthemanagerthathewasanhonestman.
7.否定的转移
若主句谓语动词为think,consider,suppose,believe,expect,fancy,guess,imagine等,其后的宾语从句若含有否定意义,一般要把否定词转移到主句谓语上,从句谓语用肯定式。例如:
Idon’tthinkthisdressfitsyouwell.我认为这件衣服不适合你穿。
高一英语语法4
since的四种用法
1) since +过去一个时间点 (如具体的年、月、日期、钟点、1980, last month, half past six)。 I he been here since 1989.
2) since +一段时间+ ago
I he been here since five months ago.
3) since +从句
Great changes he taken place since you left.
Considerable time has elapsed since we he been here.
高一英语语法5
1.because of因为……(注意和because 的区别)
2.even if(=even thoug)即使,用来引导让步状语从句
3e up走上前来,走近,发生,出现 come up with 追上,赶上,提出
4municate with sb和某人交流
5.be different from…与……不同
be different in…在……方面不同
Most of my projects are different in performance.我多数作品的演奏风格都不同。
6.be based on以……为基础
7.at present目前,眼下for the present眼前;暂时
8.make(good/better/full)use of
9.the latter后者 the former前者
10.a large number of大量的 the number of…的数量
11.such as例如
12.hold on坚持住,握住不放;(打电话时)等—会
13.…you will hear the difference in the way(that/in which)people speak.
你会听出人们在说话时的差异。
14.play a role/part(in)在…中担任角色;在…中起作用;扮演一个角色
15.the same…as…与……一样
16.at the top of…在…顶上
at the bottom of在……底部
17.bring up教养,养育;提出
18.request sb(not)to do sth.要求某人做/不要做某事
19.be satisfied with…对……感到满意,满足于
20.suggest v.(request,insist…)
I suggested you do what he says.我建议你按照他说的去做。
I suggest you not go tomorrow.我想你明天还是不要去了。
His pale face suggested that he was in bad health.他苍白的脸色暗示了他身体不好。
注意:insist 意思为“坚持要求”时后面的that从句用虚拟语气;如果insist 意为“强调,坚持认为”的时候,从句可以用任何所需要的时态。例如:She insisted that she didn’t tell a lie.她坚持认为她没撒谎。
21.according to…按照…根据…
拓展阅读:高一学生基础差怎么学英语1、词汇积累。高一学生想要学好英语,首先需要掌握足够多的词汇量,只有认识了才能理解,理解好了才能应用。所以在积累词汇的同时还要注意词汇的用法,这是高一学生需要注意的,因为即使是同一个单词,在特定的环境和语句中都可能会有不同的意思。
2、预习和复习。对于高一学生来说,不管学习任何一门科目,预习和复习都是必须的。预习可以让你了解到明天英语课堂要讲什么知识,提高英语课堂听课效率。课后复习可以让你对英语课堂上讲解的重点知识加以巩固,加深自己的所学知识的记忆。
3、课堂笔记。对于高一学生来说,英语老师在课堂上讲的每一个知识点都是重点,所以要认真的记录课堂笔记。这样一来可以加深记忆,二来可以作为以后复习的资料,当然课堂笔记的记录内容,可以根据自身情况来定。
4、阅读。阅读是高中英语的一个重要部分。阅读一直考察的是高中学生综合能力,高一学生想要提高阅读能力不是仅靠刷题就可以的。根据自身的情况每天做几道阅读题,做完后认真对照答案,仔细思考解题思路。
全部倒装与部分倒装有什么区别?
高中英语语法知识归纳
名词性从句重难点
1. 在名词性从句中,疑问句要用陈述句的语序。例如:
①Can you make sure ____the gold ring ?(MET90)
A.where Alice had put D.where has Alice put
2. 动词 dou 用在疑问句或否定句中,其后宾语从句常用 that 作连接词;用在肯定句中,连接词用 whether 或 if 皆可,而不用 that。
3. 否定转移问题。
①将think, believe, suppose, expect, fancy, guess, imagine等动词后面跟宾语从句时否定转移 我想我并不认识你。 我相信他不回来。
We dont expect he will come tonight , will he ?
注意:若谓语动词为hope,宾语从句中的否定词不能转移。 I hope you werent ill. 我想你没有生病吧。
②将seem, ear 等后的从句的否定转移
看来他们不知道往哪去。
看来我们明天不会碰上好天气。
4. 主谓一致问题。 . .
5. 语气问题
① 在含有 suggest , order , demand , propose , command , request , insist, desire, require, advise 等表示要求、命令、建议、决定等意义的动词后,that从句常用“should+ 动词原形”的结构 我建议我们应该立刻出发。
② 在It is +过去分词+that的主语从句中 decided,demanded,desired,insisted,ordered,proposed,suggested,recommended,requested, required等。
It is desired that we(should)get everything ready this evening.
③ 在表语从句或同位语从句中
The suggestion that the mayor (should) present the prizes was accepted by everyone.
高中英语语法常考知识
一、名词可数与不可数及修饰词:
常考的抽象名词有:advice, chalk, furniture, patience, paper, clothing, fun, power, work, oil, jewelery, homework, sugar, information, salt, knowledge, luck, weather, progress, news (word), money
注意:another不能修饰不可数名词,可说another book,不可说another news。
二、复合名词的复数形式因词而异:
1. a man driver (men drivers) a woman doctor ( women doctors)
2. a film-goer (film-goers) **爱好者
3. a looker-on (lookers-on) 旁观者 passers-by
4. a grown-up (grown-ups) 成年人
三、部分名词的复数形式表示特殊意义:
goods, looks(表情、外貌), manners, papers, greens(青菜、蔬菜), irons(熨斗), forces(军队), sands(做作的样子、架子) →put on airs 3. Wood can be made into paper.
He likes going out for fresh air.
四、
1. 单复数相同:sheep, deer, fish, Chinese, Japanese, means, works
2. 只有复数:cattle, people
3. 常以复数形式出现:trousers, glasses, thanks, clothes, remains(遗物), contents, goods, congratulations, means, sports, preparations(准备), tears, repairs, regards, games(运动会)
4. 以s结尾的学科或专有名词常作单数:
politics, maths, physics, the United States, The United Nations
五、几组易错名词的.用法:
1. many a + 单数名词 = many + 复数名词
2. 集合名词:family, team, audience, enemy, public, group, class, , company, police, party 作主语时,若看作一个整体时,谓语动词用单数;若表示组成分子,则用复数。
e.g. The police are on duty at the street corner.
My family is / are going to he a long journey.
3. population:
1)作为“人口”的总称或“居民”的总数是不可数名词,谓语用单数。
2)问“多少人口”时,不说how many或how much,而用what。
3)在谈到“人口比多”时,常用large,great;“人口少”时,常用small,而不用much,little。
4)当谈及“有人口”时, 习惯上用he a population of。
5)当“百分数/分数+ of the population”作主语时,谓语用复数。
6)表示某个地区人口时,其前应有定冠词。
7)population不能与people连用。
e.g. The population in China is very large, and 80% of the population are farmers.
The city has a population of the million.
高中英语语法知识
1.名词(nouns)n.:
名词是词性的一种,也是实词的一种,是指代人、物、事、时、地、情感、概念等实体或抽象事物的词。名词可以独立成句。在短语或句子中通常可以用代词来替代。名词可以分为专有名词(Proper Nouns)和普通名词 (Common Nouns),专有名词是某个(些)人,地方,机构等专有的名称,如Beijing,China等。普通名词是一类人或东西或是一个抽象概念的名词,如:book,sadness等。
2.代词(pronoun)pron.:
代词是代替名词的一种词类。大多数代词具有名词和形容词的功能。英语中的代词,按其意义、特征及在句中的作用分为:人称代词、物主代词、指示代词、反身代词、相互代词、疑问代词、关系代词、连接代词和不定代词九种。
3.数词(numeral)Num.:
表示“多少”和“第几”的词,叫数词。其用法相当于名词或者形容词。数词分为基数词和序数词两种。
4.形容词(adjective)adj.或a.;
很多语言中均有的主要词类中的一种。主要用来修饰名词的词,表示事物的特征。形容词用来修饰名词或代词,表示人或事物的性质、状态,和特征的程度好坏,与否。
5.副词(adverb)adv.:
是一种用来修饰动词、形容词、全句的词,说明时间、地点、程度、方式等概念的词。副词是一种半虚半实的词。副词可分为:时间副词、地点副词、方式副词、程度副词、疑问副词、连接副词、关系副词、频率副词和说明性副词等。
6.动词(Verb)v.:
动词,就是用来形容或表示各类动作的词汇。基本上每个完整的句子都有一个动词,要表示第二个动作时可使用不定词、动名词、对等连接词、从属连接词或增加子句等方法连结。
英语中的全部倒装与部分倒装我还是比较熟悉的,毕竟也是一次性通过大学英语四六级考试的过来人~~对于这两个英语语法知识点,我们逐一去突破~~
一、全部倒装(完全倒装)
定义:倒装英语句子的主语通常位于谓语动词之前,这种语序被称为正常语序。但有时出于修辞或某种特殊的语法结构的需要,需要将谓语动词放在主语之前,这种语序则叫倒装语序。主语和谓语完全倒置叫完全倒装。
完全倒装的基本形式是“谓语+主语”,主要见于以下情况:
1、here和there位于句首时的倒装:表示地点的here和there位于句首时,其后用完全倒装形式。这类倒装句的谓语通常是动词be和come,go等表示移动或动态的不及物动词:
如:Here's Tom.?汤姆在这里。
Here comes the bus.?公共汽车来了。?
There goes the last train.?最后一班火车开走了。
2、away和down等位于句首时的倒装:地点副词away, down, in, off, out, over, round, up等位于句首时,其后用完全倒装语序。这类倒装句的谓语通常表示动态的不及物动词:
如:Away went the runners. 赛跑选手们跑远了。
Round and round flew the plane. 飞机盘旋着。
Down came the rain and up went the umbrellas.?下雨了,伞都撑起来了。
3、某些状语或表语位于句首时的倒装:为了保持句子平衡或使上下文衔接紧密,有时可将状语或表语置于句首,句中主语和谓语完全倒装。
如:Among these people was his friend Jim.?他的朋友吉姆就在这些人当中。
By the window sat a young man with a magazine in his hand.?窗户边坐着一个年轻人,手里拿着一本杂志。
4、现在分词、过去分词或不定式置于句首的倒装。有时为了强调,可将谓语部分的现在分词、过去分词或不定式置于句首,从而构成倒装:
如:Buried in the sands was an ancient village.?一个古老的村庄被埋在这沙土之中。
Standing beside the table was his wife.?站在桌旁的是他的妻子。
二、部分倒装
定义:谓语的一部分(通常是助动词/连系动词be/情态动词)位于主语前时,此时该句子的结构为部分倒装。
部分倒装的常用结构:
1、so/either(nor)意为:“也....../也不......”时。
例如:I he never been to Shanghai. Neither/Nor has she.我从来没去过上海,她也没有。
(该句中的he been to意为“曾经到过某地”为现在完成时的语法结构。第二句中为部分倒装,该句中用了neither/nor,因此常与部分倒装搭配。Has提到了主语she的前面,而neither与nor还是保持在自己原来的位置。)
2、never/no/seldom/barely/hardly/scarcely/rarely/little/nowhere/by no means/in no way/at no time等表示否定意义的副词或介词短语置于句首时。
Hardly could I believe my own eyes.? 我几乎不敢相信自己的眼睛。
(该句中具有否定意思的hardly位于句首,因此该句用的是部分倒装。情态动词位于主语的前面。)
3、not only......but(also)....../neither......nor......连接并列的句子且位于句首时。注意not only/neither和nor后的句子要部分倒装,但but(also)后面的句子不倒装。
例如:
Neither he we seen him, and nor he we heard from him.我们最近既没看见他,也没有收到他的来信。
(该句为部分倒装,在neither......nor......“既不......也不......”的句型中前后两句都要用倒装句型。所以同学们要注意和上一句Not only......but.....的句型区分开,这种结构只能是前句用倒装,后句不用倒装。)
上一篇:名人名言推荐语_名人名言语文









